Petrogenesis and implications of the Dupangling compound granite in southern Hunan Province, China: Constraints from mineralogical chemistry, zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotope
-
摘要: 文章对位于南岭西段湘桂交界处的都庞岭东侧岩体开展了锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学、岩石学、矿物化学、岩石地球化学和Sm-Nd、Lu-Hf同位素分析研究。锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年结果显示,粗中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩年龄为215.6±2.1 Ma,中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩年龄为220.5±1.8 Ma,中粒环斑黑云母二长花岗岩年龄为222.8±1.5 Ma,结合以往研究获得的细粒白云母二长花岗岩年龄209.7±3.1 Ma,认为岩体侵位时限介于222.8~209.7 Ma,为印支期岩浆活动产物,非以往认为的燕山期。环斑钾长石、黑云母聚晶的矿物化学特征表明环斑黑云母二长花岗岩形成过程中岩浆温度、压力、成分发生震荡变化,在玄武质岩浆的底侵作用下发生多次熔融作用形成黑云母聚晶。都庞岭黑云母二长花岗岩具有较高的SiO2和K2O+Na2O含量,A/CNK值为1.02~1.39,里特曼指数(δ)为0.93~2.18,属过铝质钙碱性系列;微量元素地球化学性质表现为富集REE、Rb、Th和U及较高的HFSE(Nb、Y和Ga),亏损Ba、Sr、Eu,具有高的TFeO/MgO、Ga/Al比值,地球化学特征显示为A型花岗岩;Nd同位素εNd(t)值为-8.74~-8.13,T2DM值为1.71~1.66 Ga;锆石Hf同位素εHf(t)值为-14.1~-1.4,T2DM值为2.14~1.34 Ga,显示都庞岭黑云母二长花岗岩主要源于古老地壳物质的部分熔融,并受到了一定程度的亏损地幔物质的混染。印支运动的变质峰期在258~243 Ma,233 Ma以后华南地区处于伸展的构造背景并受到幔源玄武质岩浆大范围底侵,诱发地壳物质重熔形成伸展背景下的都庞岭印支期铝质A型(环斑)花岗岩。Abstract: In this paper, zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology, petrology, mineral chemistry, petrogeochemistry, Sm-Nd and Lu-Hf isotopes were studied for the eastern part of the Dupangling pluton, which is located at the western section of Nanling at the junction of Hunan and Guangxi provinces. The zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating results show that the age of coarse-to-medium-grained porphyritic biotite monzogranite is 215.6±2.1 Ma, medium-grained porphyritic biotite monzogranite 220.5±1.8 Ma, medium-grained rapakivi biotite monzogranite 222.8±1.5 Ma. Combined with the age of fine-grained muscovite monzogranite as 209.7±3.1 Ma obtained in the previous research, it is suggested that the emplacement time ranges from 222.8 Ma to 209.7 Ma, and the pluton is derived from the Indosinian magmatic activity rather than the Yanshanian as previously thought. The mineral-chemical characteristics of rapakivi K-feldspar and biotite phenocryst indicate that the magma temperature, pressure and composition have gone through fluctuation during the formation process, and biotite phenocryst was formed by multiple melting under the underplating by basaltic magma in this area. The Dupangling biotite monzogranites have higher contents of SiO2 and K2O+Na2O, A/CNK value ranges between 1.02 and 1.39 and Rittman index (δ) between 0.93 and 2.18, belonging to the peraluminous calc-alkaline. Moreover, these monzogranites are enriched in REE, Rb, Th and U with higher content of HFSE (Nb, Y and Ga), depleted in Ba, Sr and Eu with higher ratios of TFeO/MgO and Ga/Al, showing the characterisitics of A-type granite. The isotope εNd(t) value ranges from -8.74 to -8.13, and the T2DM value from 1.71 to 1.66 Ga; the zircon isotope εHf(t) value ranges from -14.1 to -1.4, and the T2DM value from 2.14 to 1.34 Ga. It reveals that the Dupangling biotite monzogranites mainly originated from the partial melting of ancient crustal materials and were mixed with a certain degree of depleted mantle materials. The metamorphic peak period of the Indosinian movement is from 258 Ma to 243 Ma. South China was in an extensional tectonic setting after 233 Ma and mantle-derived basalt magma was in a wide range of underplating, which caused the crustal material remelting to form the Dupangling Indosinian aluminous A-type granite (rapakiwi granite) under an extensional background.
-
Key words:
- Dupangling pluton /
- rapakiwi granite /
- SHRIMP U-Pb age /
- mineral chemistry /
- A-type granite /
- extensional setting
-
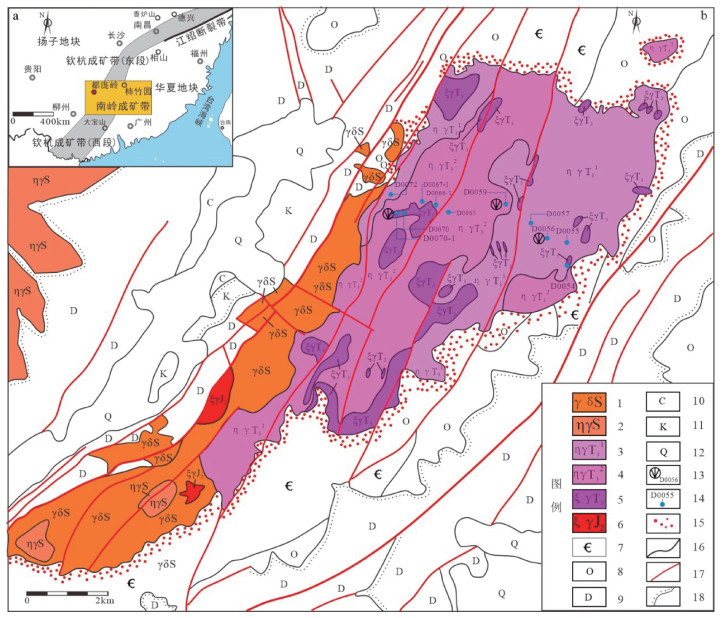
图 1 湘南都庞岭岩体所处大地构造位置及都庞岭岩体地质简图(据徐德明等,2017修改)
1—志留纪花岗闪长岩;2—志留纪二长花岗岩;3—印支期粗中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;4—印支期中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;5—印支期中粒环斑黑云母花岗岩;6—燕山期中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;7—寒武系;8—奥陶系;9—泥盆系;10—石炭系;11—白垩系;12—第四系;13—同位素年龄点(D0056、D0059和D0070-1);14—样品采样位置;15—角岩化带;16—地质界线;17—断裂;18—角度不整合界线
a—都庞岭岩体大地构造位置;b—都庞岭岩体地质简图Figure 1. Tectonic position and geological sketch of the Dupangling pluton in the south of Hunan(modified from Xu et al., 2017)
(a) Tectonic position; (b) Geological sketch
1-Silurian granodiorite; 2-Silurian monzogranite; 3-Indosinian coarse-to-medium-grained porphyritic biotite monzogranite; 4-Indosinian medium-grained porphyritic biotite monzogranite; 5-Indosinian medium-grained rapakivi biotite syenogranite; 6-Yanshanian medium-grained porphyritic biotite monzogranite; 7-Cambrian system; 8-Ordovician system; 9-Devonian system; 10-Carboniferous system; 11-Cretaceous system; 12-Quaternary system; 13-Sample locations for isotopic age analysis (D0056, D0059, and D0070-1); 14-Sample locations; 15-Hornfelsic zones; 16-Geologic boundary; 17-Fracture; 18-Angular unconformity boundary图 2 都庞岭黑云母二长花岗岩、黑云母斑晶集合体岩石学特征
a—灰白色粗中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩(斑晶含量约15%);b—中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩与粗中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩呈脉动接触;c—中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩(黑云母含量较低);d—灰白色中粒环斑黑云母二长花岗岩中环斑晶含量约20%(钾长石环斑呈卵球状);e—中粒环斑黑云母二长花岗岩中发育的环斑钾长石见斜长石环边; f—中粒环斑黑云母二长花岗岩中钾长石见震荡环带(背散射图像);g—粗中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩中见黑云母斑晶集合体;h—粗中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩中见黑云母斑晶呈不均匀特征(局部含量达45%);i—黑云母斑晶中见石英、绢云母等细小矿物(背散射图像)
Figure 2. Petrological characteristics of the Dupangling biotite monzogranite and biotite phenocryst aggregate
(a) Gray-white coarse-to-medium-grained porphyritic biotite monzogranite (Phenocryst content is about 15%); (b) Pulsating contact between medium-grained porphyritic biotite monzogranite and coarse-to-medium-grained porphyritic biotite monzogranite; (c) Characteristics of medium-grained porphyritic biotite monzogranite (Biotite content is low); (d) Phenocryst content is about 20% in gray-white medium-grained rapakivi biotite monzogranite (The rapakivi texture of potassium feldspar is ovoid); (e) Rapakivi potassium feldspar with medium-grained marginal ring plagioclase developed in the medium-grained rapakivi biotite monzogranite; (f) Back-scattered electron image of potassium feldspar with oscillatory zoning in the medium-grained rapakivi biotite monzogranite; (g) Biotite phenocryst aggregates in coarse-to-medium-grained porphyritic biotite monzogranite; (h) Biotite phenocryst with heterogeneous characteristics in coarse-to-medium-grained porphyritic biotite monzogranite (Local content is up to 45%); (i) Back-scattered electron image of fine minerals such as quartz and sericite in biotite phenocryst
图 4 都庞岭斑状黑云母二长花岗岩中钾长石Or-Ab-An分类图解(Smith, 1974)
Figure 4. Or-Ab-An diagram for the potassium feldspar in the Dupangling porphyrite biotite monzogranite (Smith, 1974)
图 5 都庞岭斑状黑云母二长花岗岩中黑云母的成分分类图(Foster, 1960)
A—金云母;B—镁质黑云母;C—铁质黑云母;D—铁叶黑云母;E—铁白云母;F—白云母
Figure 5. Diagram showing the biotite composition in the Dupangling porphyritic biotite monzogranite (Foster, 1960)
A-Phlogopite; B-Magnesian biotite; C-Ferric biotite; D-Siderophyllite; E-Ferrimuscovite; F-Muscovite
图 7 都庞岭黑云母二长花岗岩岩石化学图解
a—TAS分类图解(据Cox et al., 1979;Wilson, 1989修改);b—Na2O-K2O图解;c—A/CNK-A/NK图解(Maniar and Piccoli, 1989);d—SiO2-[(Na2O+K2O)-CaO] 图解(Frost,2001)
Figure 7. Petrochemical diagrams for the Dupangling biotite monzogranite
(a) TAS classification diagram(Schema is modified from Cox et al., 1979; Wilson, 1989); (b) Na2O-K2O diagram; (c) A/CNK-A/NK diagram(Schema from Maniar and Piccoli, 1989); (d) SiO2-[(Na2O+K2O)-CaO] diagram(Schema from Frost, 2001)
图 8 都庞岭岩体微量元素原始地幔蛛网图和稀土元素球粒陨石配分模式图(典型A型花岗岩的微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图和REE球粒陨石标准化图(蓝色)分布区域据张旗,2012修改;标准化数据引自Sun and Mcdonough, 1989)
a—微量元素原始地幔蛛网图;b—稀土元素球粒陨石配分模式图
Figure 8. Primitive mantle spider diagram for trace elements and chondrite partition pattern diagram for rare earth elements of the Dupangling pluton (Primitive mantle spider diagram of trace elements and REE chondrite standardized map (blue) of typical A-type granite are modified from Zhang, 2012; Standardized data are quoted from Sun and Mcdonough, 1989)
(a) Primitive mantle spider diagram for trace elements; (b) Chondrite partition pattern diagram for rare earth elements
图 9 都庞岭东侧岩体岩石类型判别图解
a—A型花岗岩的SiO2-TFeO/MgO判别图解(Whalen et al., 1987);b—A型花岗岩的K2O-Na2O判别图解(Collins et al., 1982)
Figure 9. Discrimination diagram for the rock-type of the eastern part of the Dupangling pluton
(a) SiO2-TFeO/MgO discrimination diagram for A-type granite (Schema from Whalen et al., 1987); (b) K2O-Na2O discrimination diagram for A-type granite (Schema from Collins et al., 1982)
图 10 都庞岭东侧岩体岩石类型判别图解
a—A型花岗岩的10000×Ga/Al-Nb判别图解(Whalen et al., 1987);b—A型花岗岩的10000×Ga/Al-TFeO/MgO判别图解(Whalen et al., 1987)
Figure 10. Discrimination diagram for the rock-type of the eastern part of the Dupangling pluton
(a) 10000×Ga/Al-Nb discrimination diagram for A-type granite(Schema from Whalen et al., 1987); (b) 10000×Ga/Al-TFeO/MgO discrimination diagram for A-type granite(Schema from Whalen et al., 1987)
图 11 都庞岭岩体印支期花岗岩εHf(t)-t关系图
(华夏基底数据引自Yu et al., 2010;扬子基底数据引自Wang et al., 2010和何苗等,2018;三条虚线代表的地壳演化趋势线于津海等,2007)
Figure 11. εHf(t)-t diagram for the Indosinian Dupangling granite (Huaxia base data from Yu et al., 2010; Yangtze base Data from Wang et al., 2010 and He et al., 2018; The three dotted lines which represent crustal evolution trend from Jin et al., 2007)
图 12 都庞岭二长花岗岩中黑云母的TFeO/(TFeO+MgO)-MgO图解(周作侠,1988)
Figure 12. TFeO/(TFeO+MgO)-MgO diagram for the biotite in the Dupangling monzonite granite
图 13 Nb-Y及Rb-Yb+Ta环境判别图解(Pearce,1996)
WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋脊花岗岩;VAG—火山弧花岗岩;syn-COLG—同碰撞花岗岩;post-COLG—后碰撞花岗岩
a—Nb-Y环境判别图解;b—Rb-Yb+Ta环境判别图解Figure 13. Environmental discrimination diagrams of Nb-Y and Rb-Yb+Ta(Pearce, 1996)
(a) Nb-Y diagram; (b)Rb-Yb+Ta diagram
WPG-Intraplate granite; ORG-Ridge granite; VAG-Volcanic arc granite; syn-COLG-Syn-collisional granite; post-COLG-Post-collisional granite表 1 都庞岭花岗岩主要造岩矿物含量及副矿物含量表(%)
Table 1. Contents of major rock-forming minerals and accessory minerals of the Dupangling granite (%)
类型/矿物 石英 钾长石 斜长石 黑云母 磁铁矿 磷灰石 粗中粒斑状黑云母二长 30~36 32~35 28~33 2~3 1~3 <1 花岗岩 均值 33 34 31 3 2 中粒斑状(环斑)黑 33~38 30~35 25~30 2~3 1~3 <1 云母二长花岗岩 均值 35 33 27 2 2 表 2 都庞岭斑状黑云母二长花岗岩黑云母化学组成电子探针分析结果
Table 2. Electron probe analysis results of the biotite chemical composition of the Dupangling porphyritic biotite monzogranite
样品号 D0066-1-1 D0066-1-1 位置 黑云母斑晶1 黑云母斑晶2 黑云母基质1 黑云母基质2 点号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 单位:% SiO2 37.19 37.65 37.4 36.92 37.14 37.00 37.67 37.49 37.70 37.51 37.45 38.01 37.69 37.75 37.84 36.98 37.34 37.6 37.87 37.49 37.92 37.52 37.49 37.55 37.21 TiO2 3.68 3.05 3.47 4.09 4.59 4.27 3.26 2.44 3.35 3.56 4.08 3.07 3.41 4.31 2.89 2.77 3.63 4.26 4.08 3.58 2.90 4.09 3.49 4.08 4.61 Al2O3 13.97 14.51 14.20 13.54 13.56 13.69 14.03 14.69 13.88 13.92 13.62 14.22 13.74 13.53 14.45 13.69 13.66 13.31 13.47 13.95 14.64 13.84 14.26 13.97 13.65 TFeO 22.27 22.37 22.95 22.68 22.91 22.46 22.35 22.29 23.36 23.45 23.41 22.94 23.04 23.28 23.70 22.57 23.48 23.08 22.84 22.96 23.10 22.84 22.81 23.09 22.87 MnO 0.32 0.31 0.35 0.24 0.32 0.35 0.37 0.22 0.28 0.34 0.33 0.30 0.35 0.35 0.38 0.46 0.28 0.35 0.27 0.31 0.32 0.37 0.41 0.37 0.35 MgO 4.50 4.74 4.70 4.29 4.27 4.22 4.62 4.75 4.55 4.27 4.26 4.80 4.64 4.39 4.47 4.88 4.66 4.47 4.53 4.67 4.51 4.40 4.54 4.36 4.11 CaO 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.03 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.08 0.10 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.03 0.00 0.01 K2O 11.44 11.61 11.51 11.39 11.31 11.44 11.75 11.66 11.61 11.60 11.61 11.64 11.68 11.30 11.49 11.50 11.65 11.60 11.65 11.73 11.71 11.70 11.69 11.67 11.53 Cl 0.09 0.09 0.10 0.08 0.09 0.09 0.08 0.09 0.09 0.08 0.09 0.08 0.09 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.09 0.08 0.10 0.09 0.09 0.05 0.09 0.06 0.10 F 0.00 0.12 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.15 0.10 0.19 0.00 0.00 0.16 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.09 0.06 0.00 0.12 0.08 0.03 0.01 0.03 0.00 0.00 以23个氧原子计算的阳离子数 Si 5.95 5.96 5.92 5.94 5.91 5.93 5.99 5.98 5.97 5.95 5.94 5.98 5.98 5.96 5.96 5.97 5.92 5.96 5.99 5.94 5.96 5.93 5.93 5.92 5.91 AlIV 2.05 2.04 2.08 2.06 2.09 2.07 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.05 2.06 2.02 2.02 2.04 2.04 2.03 2.08 2.04 2.01 2.06 2.04 2.07 2.07 2.08 2.09 AlVI 0.58 0.67 0.57 0.51 0.46 0.51 0.61 0.74 0.56 0.55 0.48 0.62 0.54 0.47 0.64 0.57 0.48 0.44 0.49 0.54 0.68 0.51 0.59 0.52 0.47 Ti 0.44 0.36 0.41 0.49 0.55 0.51 0.39 0.29 0.4 0.42 0.49 0.36 0.41 0.51 0.34 0.34 0.43 0.51 0.48 0.43 0.34 0.49 0.42 0.48 0.55 Fe2+ 2.53 2.41 2.47 2.63 2.74 2.64 2.41 2.31 2.51 2.56 2.61 2.44 2.45 2.77 2.52 2.27 2.43 2.6 2.60 2.42 2.45 2.54 2.44 2.57 2.70 Fe3+ 0.45 0.55 0.57 0.42 0.31 0.37 0.57 0.66 0.59 0.55 0.50 0.58 0.60 0.31 0.60 0.78 0.69 0.46 0.42 0.62 0.59 0.48 0.58 0.48 0.35 Mn 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 Mg 1.07 1.12 1.11 1.03 1.01 1.01 1.09 1.13 1.07 1.01 1.01 1.13 1.10 1.03 1.05 1.17 1.10 1.06 1.07 1.10 1.06 1.04 1.07 1.03 0.97 Ca 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 K 2.33 2.34 2.32 2.34 2.30 2.34 2.38 2.37 2.35 2.35 2.35 2.34 2.36 2.27 2.31 2.37 2.36 2.35 2.35 2.37 2.35 2.36 2.36 2.35 2.34 Cl 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.03 F 0.00 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.05 0.10 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.03 0.00 0.06 0.04 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.00 0.00 OH 3.98 3.92 3.97 3.98 3.98 3.98 3.90 3.93 3.88 3.98 3.98 3.9 3.95 3.98 3.98 3.93 3.95 3.98 3.91 3.94 3.96 3.98 3.96 3.98 3.97 TFe/(TFe+Mg) 0.74 0.73 0.73 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.73 0.72 0.74 0.75 0.76 0.73 0.74 0.75 0.75 0.72 0.74 0.74 0.74 0.73 0.74 0.74 0.74 0.75 0.76 Fe3+/TFe 0.15 0.19 0.19 0.14 0.10 0.12 0.19 0.22 0.19 0.18 0.16 0.19 0.20 0.10 0.19 0.26 0.22 0.15 0.14 0.20 0.19 0.16 0.19 0.16 0.11 Mg/(Mg+Fe) 0.26 0.27 0.27 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.27 0.28 0.26 0.25 0.24 0.27 0.26 0.25 0.25 0.28 0.26 0.26 0.26 0.27 0.26 0.26 0.26 0.25 0.24 表 3 都庞岭环斑黑云母二长花岗岩钾长石化学组成电子探针分析结果
Table 3. Electron probe analysis results of the chemical composition of potassium feldspar in the Dupangling rapakivi biotite monzogranite
样品号 D0072 位置 钾长石:斑晶 点号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 单位:% SiO2 64.37 64.66 64.62 64.49 65.26 64.43 64.96 65.11 65.00 64.36 64.08 65.00 65.15 64.74 64.56 65.11 65.10 64.73 64.95 TiO2 0.03 0.05 0.04 0.02 0.00 0.04 0.04 0.00 0.03 0.04 0.08 0.05 0.00 0.03 0.02 0.00 0.06 0.01 0.00 Al2O3 18.15 18.28 18.19 18.20 18.09 18.10 18.27 18.19 18.14 17.96 18.17 18.19 18.45 18.40 18.17 18.15 18.21 17.83 18.12 FeO 0.07 0.07 0.10 0.06 0.05 0.06 0.05 0.09 0.10 0.05 0.05 0.09 0.07 0.09 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.04 0.00 MnO 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.02 MgO 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 CaO 0.05 0.11 0.11 0.13 0.00 0.00 0.14 0.11 0.07 0.00 0.03 0.09 0.15 0.09 0.03 0.08 0.13 0.02 0.03 Na2O 1.54 2.29 2.04 2.21 1.85 0.54 2.76 2.97 2.29 0.54 0.89 2.83 2.83 2.48 0.83 2.70 2.65 1.22 0.95 K2O 14.86 13.92 14.05 14.14 14.33 16.64 12.94 12.89 13.82 16.41 15.37 13.08 12.67 13.50 16.02 13.38 13.11 15.52 15.86 BaO 0.48 0.64 0.44 0.49 0.24 0.44 0.41 0.48 0.45 0.18 0.59 0.37 0.38 0.53 0.52 0.36 0.35 0.17 0.05 总和 99.56 100.02 99.58 99.75 99.82 100.25 99.61 99.84 99.94 99.54 99.29 99.70 99.70 99.85 100.25 99.89 99.68 99.56 99.98 基于8个氧原子计算 Si 2.99 2.99 2.99 2.99 3.01 2.99 2.99 3.00 3.00 3.00 2.99 2.99 2.99 2.99 2.99 3.00 3.00 3.01 3.00 Al 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.98 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.99 1.00 0.99 1.00 1.00 0.99 0.98 0.99 0.98 0.99 Ca 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 Na 0.14 0.21 0.18 0.20 0.16 0.05 0.25 0.26 0.20 0.05 0.08 0.25 0.25 0.22 0.07 0.24 0.24 0.11 0.09 K 0.88 0.82 0.83 0.84 0.84 0.99 0.76 0.76 0.81 0.98 0.92 0.77 0.74 0.79 0.95 0.79 0.77 0.92 0.94 Ba 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 Or 86.17 79.56 81.46 80.28 83.60 95.34 75.01 73.69 79.60 95.22 91.81 74.92 74.10 77.84 92.56 76.20 76.02 89.24 91.55 Ab 13.61 19.93 18.01 19.11 16.38 4.66 24.31 25.81 20.05 4.78 8.04 24.63 25.18 21.71 7.31 23.40 23.36 10.65 8.33 An 0.22 0.51 0.53 0.61 0.02 0.00 0.67 0.50 0.35 0.00 0.16 0.45 0.72 0.45 0.14 0.40 0.62 0.12 0.13 表 4 都庞岭环斑黑云母二长花岗岩钾长石化学组成电子探针分析结果
Table 4. Electron probe analysis results of the chemical composition of potassium feldspar in the Dupangling rapakivi biotite monzogranite
样品号 D0070-2-1 位置 钾长石:基质矿物 点号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 单位:% SiO2 65.12 64.61 65.06 64.80 65.26 64.81 65.00 65.03 65.21 64.98 64.73 64.58 TiO2 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.00 Al2O3 18.07 17.96 18.13 18.04 17.95 17.89 17.84 18.12 18.01 17.90 18.00 17.91 FeO 0.03 0.01 0.06 0.03 0.09 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.01 0.03 0.06 0.04 MnO 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 MgO 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 CaO 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Na2O 0.50 0.51 0.54 0.55 0.45 0.48 0.39 0.37 0.46 0.36 0.44 0.35 K2O 16.76 16.39 16.51 16.55 16.70 16.49 16.73 16.90 16.76 17.05 16.68 16.57 BaO 0.03 0.13 0.00 0.00 0.07 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.05 0.01 0.00 总和 100.55 99.65 100.32 100.01 100.53 99.73 99.96 100.45 100.49 100.40 99.96 99.46 基于8个氧原子计算 Si 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.01 3.01 3.01 3.00 3.01 3.01 3.00 3.01 Al 0.98 0.98 0.99 0.99 0.98 0.98 0.97 0.99 0.98 0.98 0.98 0.98 Na 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.03 K 0.99 0.97 0.97 0.98 0.98 0.98 0.99 1.00 0.99 1.01 0.99 0.98 Ba 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Or 95.68 95.40 95.22 95.14 96.05 95.77 96.57 96.75 95.96 96.93 96.14 96.90 Ab 4.30 4.53 4.69 4.83 3.95 4.23 3.43 3.25 4.04 3.07 3.86 3.10 An 0.02 0.07 0.09 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 表 5 都庞岭黑云母二长花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 5. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb isotopic analysis results of the Dupangling biotite monzogranite
测试点 206Pbc/% 元素含量/(μg/g) Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 不一致性/% U Th 206Pb* 207Pb*/206Pb* ±/% 207Pb*/235U ±/% 206Pb*/238U ±/% 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 样号:D0056粗中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩 D0056-1 1.77 3259 544 103.0 0.17 0.0508 3.3 0.2520 3.5 0.03598 1.2 227.9 ±2.8 233.0 ±21.0 2 D0056-2 0.41 338 218 9.8 0.67 0.0514 2.9 0.2387 3.2 0.03365 1.4 213.4 ±2.9 209.3 ±5.1 18 D0056-3 3.01 413 258 12.3 0.65 0.0512 12.1 0.2380 12.1 0.03367 1.5 213.5 ±3.1 204.0 ±17.0 14 D0056-4 2.30 361 248 10.8 0.71 0.0512 8.9 0.2400 9.1 0.03395 1.5 215.2 ±3.1 196.0 ±12.0 15 D0056-5 0.41 784 379 23.0 0.50 0.0497 3.0 0.2333 3.3 0.03406 1.3 215.9 ±2.7 200.4 ±5.8 -20 D0056-7 0.12 587 353 17.1 0.62 0.0509 3.1 0.2383 3.4 0.03397 1.4 215.3 ±3.0 211.2 ±4.9 9 D0056-8 0.31 970 613 28.8 0.65 0.0499 2.4 0.2371 2.7 0.03446 1.3 218.4 ±2.7 199.8 ±4.4 -15 D0056-9 0.24 264 180 7.8 0.70 0.0504 5.4 0.2380 5.6 0.03417 1.4 216.6 ±3.1 216.5 ±9.5 -1 D0056-10 0.61 250 236 7.3 0.98 0.0512 8.9 0.2400 9.0 0.03400 1.5 215.5 ±3.2 208.6 ±9.1 13 D0056-13 2.20 501 357 15.8 0.74 0.0514 8.0 0.2550 8.1 0.03597 1.6 227.8 ±3.5 224.0 ±11.0 12 样号:D0059中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩 D0059-1 2.22 1528 552 46.2 0.37 0.0502 5.0 0.2380 5.1 0.03439 1.3 217.9 ±2.7 179.0 ±14.0 -6 D0059-3 2.05 642 477 19.4 0.77 0.0518 7.5 0.2460 7.6 0.03439 1.3 217.9 ±2.9 164.8 ±9.4 21 D0059-4 0.28 1384 633 44.3 0.47 0.0509 1.7 0.2611 2.1 0.03714 1.2 235.1 ±2.8 212.5 ±4.3 2 D0059-5 0.43 242 159 7.3 0.68 0.0497 3.4 0.2385 3.7 0.03480 1.4 220.5 ±3.1 206.5 ±6.0 -22 D0059-6 0.42 353 279 10.6 0.82 0.0524 3.2 0.2525 3.5 0.03491 1.4 221.2 ±3.0 215.2 ±5.5 27 D0059-7 0.18 321 199 9.6 0.64 0.0509 4.8 0.2440 5.0 0.03479 1.4 220.4 ±3.0 214.8 ±6.8 6 D0059-8 0.40 531 342 16.1 0.67 0.0516 2.8 0.2503 3.2 0.03519 1.4 222.9 ±3.1 157.3 ±4.8 17 D0059-10 0.23 494 298 14.6 0.62 0.0506 2.8 0.2402 3.1 0.03440 1.3 218.0 ±2.8 208.2 ±4.4 3 D0059-12 0.46 781 445 23.6 0.59 0.0511 3.1 0.2472 3.3 0.03506 1.3 222.1 ±2.8 204.6 ±5.5 10 D0059-13 0.11 543 520 16.5 0.99 0.0505 2.0 0.2458 2.4 0.03528 1.3 223.5 ±2.8 205.4 ±6.0 -2 D0059-14 0.31 561 322 16.8 0.59 0.0504 1.9 0.2422 2.3 0.03485 1.3 220.8 ±2.8 214.0 ±4.1 -3 样号:D0070-1中粒环斑黑云母二长花岗岩 D0070-1-1 0.25 415 235 12.4 0.58 0.0500 5.4 0.2390 5.6 0.03474 1.2 220.1 ±2.7 218.4 ±8.9 -14 D0070-1-2 0.00 523 312 15.7 0.62 0.0501 2.4 0.2419 2.6 0.03498 1.2 221.7 ±2.6 219.9 ±4.5 -10 D0070-1-3 - 1179 393 36.2 0.34 0.0512 1.3 0.2529 1.7 0.03580 1.1 226.7 ±2.5 222.6 ±3.9 10 D0070-1-4 0.01 324 114 9.9 0.36 0.0525 3.3 0.2596 3.5 0.03589 1.2 227.3 ±2.8 213.4 ±8.2 26 D0070-1-5 0.01 345 179 10.6 0.54 0.0513 3.3 0.2528 3.6 0.03575 1.2 226.5 ±2.7 220.0 ±6.1 11 D0070-1-6 - 474 721 14.3 1.57 0.0517 2.4 0.2512 2.7 0.03524 1.2 223.3 ±2.6 218.8 ±3.6 18 D0070-1-7 1.28 1509 699 46.4 0.48 0.0488 4.9 0.2380 5.0 0.03534 1.1 223.9 ±2.5 210.3 ±9.5 -61 D0070-1-8 0.33 626 346 18.4 0.57 0.0477 5.5 0.2250 5.6 0.03416 1.2 216.6 ±2.5 209.5 ±6.0 -163 D0070-1-11 0.00 532 350 16.1 0.68 0.0519 2.0 0.2525 2.3 0.03530 1.2 223.6 ±2.6 215.8 ±4.8 20 D0070-1-12 0.26 1126 477 34.2 0.44 0.0498 2.4 0.2420 2.7 0.03521 1.1 223.1 ±2.5 208.8 ±5.4 -19 D0070-1-13 0.33 683 308 20.6 0.47 0.0498 3.2 0.2397 3.4 0.03494 1.2 221.4 ±2.5 208.4 ±6.5 -20 D0070-1-14 1.55 494 285 15.0 0.60 0.0486 7.1 0.2330 7.2 0.03476 1.3 220.3 ±2.9 205 ±11.0 -70 注:Pbc和Pb*分别代表普通铅和放射成因铅;206Pbc指普通铅中的206Pb占全铅206Pb的百分数。 表 6 都庞岭岩体主量元素和微量元素分析结果(主量元素/%;微量、稀土元素/×10-6;Au/×10-9)
Table 6. Major and trace elements compositions of the Dupangling pluton (main elements/%, trace and REE elements/×10-6, Au/×10-9)
D0055 D0056 D0057 D0059 D0065 D0067-1 D0070 D0070-1 D0072 D0054 斑状黑云母二长花岗岩 环斑黑云母二长花岗岩 SiO2 78.15 76.11 76.11 76.99 77.03 75.57 76.08 76.69 73.82 78.51 TiO2 0.11 0.13 0.12 0.04 0.17 0.08 0.11 0.09 0.25 0.08 Al2O3 11.91 11.81 12.11 12.46 12.06 12.17 12.32 12.12 13.58 12.12 FeO 0.92 1.74 1.86 1.01 1.41 1.79 1.62 1.14 2.02 1.51 Fe2O3 1.67 2.16 2.35 1.41 1.88 2.12 1.97 1.71 2.75 2.14 MnO 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.05 0.02 MgO 0.12 0.22 0.17 0.03 0.23 0.07 0.13 0.11 0.37 0.18 CaO 0.19 0.65 0.61 0.26 0.93 0.58 0.62 0.45 0.99 0.12 Na2O 2.71 2.90 3.19 3.64 2.93 3.17 3.12 3.12 2.84 4.12 K2O 4.98 4.51 4.65 4.54 4.94 5.19 5.05 4.93 5.36 1.64 P2O5 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.06 0.02 烧失量 0.70 0.66 0.33 0.39 0.35 0.23 0.28 0.36 0.51 0.68 总和 101.52 100.96 101.58 100.82 102.00 101.03 101.36 100.76 102.60 101.14 ALK 7.69 7.41 7.84 8.18 7.87 8.36 8.17 8.05 8.22 5.76 FeOT 2.42 3.68 3.98 2.27 3.09 3.71 3.37 2.68 4.50 3.43 A/CNK 1.17 1.09 1.06 1.09 1.02 1.02 1.05 1.07 1.12 1.39 A/NK 1.21 1.22 1.18 1.14 1.18 1.12 1.16 1.15 1.29 1.42 δ 1.68 1.66 1.86 1.97 1.82 2.15 2.02 1.92 2.18 0.93 W 18.10 12.20 21.90 22.10 4.10 5.90 3.50 5.50 6.60 7.50 Sn 14.00 23.00 20.00 41.00 15.00 13.00 19.00 20.00 12.30 11.00 Mo 0.58 1.15 0.85 1.77 0.51 2.76 0.3 0.31 0.38 0.81 Bi 9.91 1.24 3.17 2.61 2.01 0.65 1.73 1.62 1.24 0.36 Cu 4.80 4.40 2.70 19.20 2.80 3.60 2.50 3.30 9.50 10.00 Pb 55.60 46.30 54.20 74.80 45.80 52.80 56.00 60.40 38.40 18.50 Zn 29.00 26.00 32.00 25.00 27.00 21.00 25.00 23.00 30.00 19.00 Sb 0.27 0.41 0.35 0.29 0.36 0.64 0.28 0.31 0.34 0.54 Cr 4.00 7.00 4.00 3.00 6.00 4.00 4.00 4.00 7.00 6.00 Ni 1.50 2.60 2.00 1.00 2.10 1.30 1.40 1.10 3.00 2.30 Co 1.30 1.50 1.40 0.50 2.00 1.00 1.20 1.00 2.90 1.30 Hg 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 V 5.00 6.00 6.00 1.00 12.00 3.00 5.00 5.00 18.00 4.00 Nb 15.80 16.60 20.90 24.50 14.30 13.40 13.90 14.00 11.60 19.20 Ta 3.73 3.71 4.56 4.25 2.87 3.01 2.82 2.72 1.71 4.78 Th 48.20 46.00 58.20 39.90 57.00 64.40 58.50 54.40 43.80 47.00 U 13.20 21.20 18.50 22.90 16.10 23.60 13.00 11.10 7.50 17.10 Zr 90.00 105.00 123.00 123.00 129.00 91.00 136.00 126.00 141.00 105.00 Hf 3.90 4.90 5.20 6.40 4.30 3.70 5.40 5.40 4.30 4.60 Rb 550.00 544.00 640.00 772.00 460.00 590.00 530.00 490.00 409.00 201.00 Cs 19.30 30.40 44.00 39.70 22.70 31.90 35.00 30.10 24.00 11.80 Sr 13.00 16.50 13.60 2.90 33.20 6.90 21.60 23.70 53.30 47.40 Ba 58.70 58.50 54.40 8.00 151.00 10.10 77.40 63.50 409.00 87.60 Li 58.60 61.30 128.50 154.00 80.10 40.40 71.90 49.50 85.80 55.20 Be 5.41 7.61 6.07 9.36 7.28 7.99 7.56 9.15 4.08 5.71 As 60.20 7.10 0.30 4.30 0.20 2.60 3.10 5.50 1.00 35.10 Ga 18.20 17.85 19.80 20.90 17.45 18.00 18.45 17.85 17.95 17.85 Sc 5.80 5.30 6.90 5.20 5.30 5.80 4.70 4.40 5.60 6.00 Au 0.001 0.001 0.001 0.001 0.001 0.001 0.001 0.001 0.001 0.001 Ag 0.15 0.03 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.04 0.14 0.13 0.04 0.03 F 710.00 1930.00 2060.00 1580.00 1570.00 1340.00 1280.00 1030.00 720.00 1040.00 Cl 60.00 50.00 50.00 80.00 90.00 90.00 100.00 70.00 90.00 50.00 Cd 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.70 0.06 0.06 0.02 B 5.00 5.00 7.00 7.00 10.00 18.00 5.00 5.00 8.00 16.00 La 24.80 26.50 36.40 7.10 48.50 35.20 32.40 28.40 35.70 24.90 Ce 73.80 62.70 87.30 26.80 108.50 86.30 75.90 66.80 85.90 62.80 Pr 7.25 7.71 10.35 2.57 12.25 10.75 8.92 8.29 8.37 7.34 Nd 26.30 28.10 39.40 11.60 43.40 39.60 32.90 30.40 29.70 28.30 Sm 6.76 8.02 10.71 4.82 9.79 10.75 9.16 8.08 5.91 9.05 Eu 0.11 0.18 0.15 0.05 0.34 0.12 0.21 0.17 0.56 0.26 Gd 7.68 9.46 11.70 6.46 9.37 11.05 8.73 8.47 5.07 10.35 Tb 1.49 1.82 2.32 1.66 1.75 2.22 1.59 1.61 0.93 2.45 Dy 11.15 12.61 15.31 12.22 11.45 13.71 10.55 10.50 5.78 17.20 Ho 2.57 2.63 3.43 2.91 2.43 2.96 2.26 2.26 1.22 3.74 Er 8.35 9.09 10.25 9.72 7.06 8.59 6.97 7.15 3.52 10.90 Tm 1.42 1.43 1.71 1.63 1.09 1.33 1.12 1.19 0.55 1.81 Yb 9.62 9.21 11.50 11.23 7.12 8.48 7.53 7.96 3.73 12.30 Lu 1.48 1.41 1.74 1.81 1.04 1.26 1.14 1.14 0.54 1.89 Y 80.20 80.80 99.90 90.60 66.70 79.30 66.10 72.10 34.90 111.00 ∑REE 263.00 261.60 342.10 191.10 330.80 311.60 265.50 254.50 222.40 304.30 δEu 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.03 0.11 0.03 0.07 0.06 0.31 0.08 L/H 1.12 1.04 1.17 0.38 2.06 1.42 1.51 1.26 2.95 0.77 注:DI—分异指数(CIPW标准矿物, %);A/CNK—铝饱和指数(Al2O3/(CaO+Na2O+K2O), 摩尔比);A/NK—碱度指数(Al2O3/(N2O+K2O), 摩尔比);ALK—全碱含量;δ—里特曼钙碱指数;L/H—LREE/HREE 表 7 都庞岭花岗岩体岩石样品的Sm-Nd同位素组成
Table 7. Sm-Nd isotopic compositions of the Dupangling granite samples
样号 Sm Nd 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd εNd(t) T2DM/Ga ×10-6 D0056 9.476 31.92 0.1796 0.512166±3 -8.74 1.71 D0059 4.376 9.913 0.2671 0.512323±6 -8.13 1.66 D0070 7.289 29.58 0.1491 0.512145±4 -8.27 1.67 D0072 6.216 30.72 0.1224 0.512102±4 -8.35 1.68 表 8 都庞岭岩体锆石Hf同位素分析结果
Table 8. The isotopic analysis results of zircon Hf of the Dupangling pluton
点号 年龄/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf ±2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM/Ma T2DM/Ma fLu/Hf 样号:D0056-斑状黑云母二长花岗岩 D0056-1 215.6 0.020377 0.000721 0.282509 0.000021 -10.8 -6.2 1103 1638 -0.98 D0056-2 215.6 0.018715 0.000655 0.282532 0.000018 -10.1 -5.5 1083 1594 -0.97 D0056-3 215.6 0.020258 0.000704 0.282466 0.000015 -10.5 -5.9 1103 1622 -0.97 D0056-4 215.6 0.030060 0.001029 0.282487 0.000017 -18.7 -14.1 1425 2136 -0.97 D0056-5 215.6 0.033720 0.001157 0.282475 0.000017 -8.8 -4.2 1027 1514 -0.98 D0056-6 215.6 0.031632 0.001083 0.282244 0.000018 -9.5 -4.9 1058 1556 -0.97 D0056-7 215.6 0.022624 0.000809 0.282522 0.000018 -7.4 -2.7 965 1421 -0.98 D0056-8 215.6 0.028110 0.000998 0.282504 0.000016 -6.8 -2.2 957 1388 -0.96 D0056-9 215.6 0.017312 0.000626 0.282563 0.000027 -12.0 -7.5 1167 1719 -0.96 D0056-10 215.6 0.034881 0.001229 0.282580 0.000021 -10.5 -6.0 1101 1623 -0.97 D0056-11 215.6 0.033261 0.001262 0.282432 0.000017 -7.5 -2.9 972 1428 -0.98 D0056-12 215.6 0.029144 0.001042 0.282474 0.000021 -10.8 -6.2 1103 1638 -0.98 D0056-13 215.6 0.020128 0.000727 0.282560 0.000024 -10.1 -5.5 1083 1594 -0.97 样号:D0070-1-中粒环斑黑云母二长花岗岩 D0070-1-1 222.8 0.019528 0.000692 0.282570 0.000025 -7.1 -2.4 957 1401 -0.98 D0070-1-2 222.8 0.019195 0.000665 0.282563 0.000018 -7.4 -2.6 966 1417 -0.98 D0070-1-3 222.8 0.033373 0.001136 0.282476 0.000016 -10.5 -5.7 1101 1615 -0.97 D0070-1-4 222.8 0.030688 0.001138 0.282500 0.000022 -9.6 -4.9 1067 1562 -0.97 D0070-1-5 222.8 0.016223 0.000576 0.282530 0.000017 -8.6 -3.8 1010 1490 -0.98 D0070-1-6 222.8 0.033771 0.001218 0.282521 0.000017 -8.9 -4.2 1040 1516 -0.96 D0070-1-7 222.8 0.034678 0.001256 0.282507 0.000016 -9.4 -4.7 1061 1547 -0.96 D0070-1-8 222.8 0.021611 0.000804 0.282537 0.000018 -8.3 -3.5 1006 1476 -0.98 D0070-1-9 222.8 0.032734 0.001206 0.282300 0.000016 -16.7 -12.0 1351 2008 -0.96 D0070-1-10 222.8 0.035717 0.001309 0.282310 0.000019 -16.3 -11.6 1341 1987 -0.96 D0070-1-11 222.8 0.022271 0.000819 0.282598 0.000024 -6.2 -1.4 921 1340 -0.98 D0070-1-12 222.8 0.030175 0.001107 0.282519 0.000019 -8.9 -4.2 1040 1519 -0.97 D0070-1-13 222.8 0.027758 0.001012 0.282538 0.000028 -8.3 -3.5 1010 1476 -0.97 D0070-1-14 222.8 0.017280 0.000636 0.282540 0.000017 -8.2 -3.4 998 1468 -0.98 -
AMELIN Y, LEE D C, HALLIDAY A N, et al., 1999. Nature of the Earth′s earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons[J]. Nature, 399(6733): 252-255. doi: 10.1038/20426 BAI D Y, CHEN B H, ZHONG X, et al., 2014. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age, geochemistry and tectonic setting of Indosinian Wutuan pluton in southwestern Hunan Province[J]. Geology in China, 41(6): 2002-2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) BONIN B, 2007. A-type granites and related rocks: evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 97(1-2): 1-29. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.12.007 CARTER A, ROQUES D, BRISTOW C, et al., 2001. Understanding Mesozoic accretion in southeast Asia: significance of Triassic thermotectonism(indosinian orogeny)in Vietnam[J]. Geology, 29(3): 211-214. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0211:UMAISA>2.0.CO;2 CHEN C H, LIU Y H, LEE C Y, et al., 2017. The Triassic reworking of the yunkai massif (South China): EMP monazite and U-Pb zircon geochronologic evidence[J]. Tectonophysics, 694: 1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.11.022 CHEN D, SHAO Y J, LIU W, et al., 2015. Petrological and geochemical characteristics of Xitian pluton in Hunan province[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 31(1): 11-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN J F, GUO X S, TANG J F, et al., 1999. Nd isotopic model ages: implications of the growth of the continental crust of southeastern China[J]. Journal of Nanjing University(Natural Sciences), 35(6): 649-658. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN X Q, LU Y F, ZOU X W, 2008. Geochemical contrasting of Doupangling and Haiyangshan granites, Guangxi[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 44(3): 34-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) COLLINS W J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J R, et al., 1982. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 80(2): 189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895 CONRAD W K, NICHOLLS I A, WALL V J, 1988. Water-saturated and-undersaturated melting of metaluminous and peraluminous crustal compositions at 10 kb: evidence for the origin of silicic magmas in the taupo volcanic zone, New Zealand, and other occurrences[J]. Journal of Petrology, 29(4): 765-803. doi: 10.1093/petrology/29.4.765 COX K G, BELL J D, PANKHURST R J, 1979. The interpretation of igneous rocks[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 1-450. DAI B Z, JIANG S Y, JIANG Y H, et al., 2008. Geochronology, geochemistry and Hf-Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of Huziyan mafic xenoliths, southern Hunan Province, South China: petrogenesis and implications for lower crust evolution[J]. Lithos, 102(1-2): 65-87. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.08.010 EBYG N, 1992. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 20(7): 641-644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2 FAN W M, WANG Y J, GUO F, et al., 2003. Mesozoic mafic magmatism in Hunan-Jiangxi provinces and the lithospheric extension[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(3): 159-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) FOSTER M D, 1960. Interpretation of the composition of trioctahedral micas[M]. Washington: United States Government Printing Office, 1-49. FROST B R, BARNES C G, COLLINS W J, et al., 2001. A geochemical classification for granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 42(11): 2033-2048. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033 FU J H, ZHANG J X, ZHONG J, 2018. The relation between the regional geochemical spatial distribution and rock, formation, mineralization in the Dupangling-Tongshanling-Jiuyishan Area[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 34(5): 35-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) GAO W L, WANG Z X, LICL, et al., 2014. Zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implication of indosinian granite from southeastern Zhejiang, South China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(6): 1055-1067. (in Chinese with English abstract) GRIFFIN W L, WANG X, JACKSON S E, et al., 2002. Zircon Chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 61(3-4): 237-269. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00082-8 GUO F, FAN W M, LIN K, et al., 1997. Sm-Nd isotopic age and genesis of gabbro xenoliths in Daoxian County, Hunan Province[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 42(21): 1814-1817. doi: 10.1007/BF02882650 HE M, LIU Q, SUN J F, et al., 2018. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance of the Xitian Indosinian granites in eastern Hunan Province, South China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(7): 2065-2086. (in Chinese with English abstract) HE X Y, FANG T H, BO H T, et al., 2022. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of Late Permian-Middle Triassic granitoids in Guobaoshan, eastern section of the eastern Tianshan mountains: Constraints from geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28 (1): 126-142. (in Chinese with English abstract) HOU K J, LI Y H, XIE G Q, 2011. Analysis method of Hf isotope of zircon by LA-MC-ICP MS and its geological application[M]//LI Y H. A new method of isotopic analysis and dating. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 40-48. (in Chinese) Hunan Institute of Geological Survey, 2004. 1∶250000 regional geological survey report of Hunan Dao County[R]. 1-335. (in Chinese) HUANG H B, 1990. Characteristics of the Dupangling granite in Guangxi[J]. Regional Geology of China. (3): 231-236. (in Chinese) JIA X H, WANG Q, TANG G J, 2009. A-type granites: research progress and implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 33(3): 465-480. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.sciencemeta.com/index.php/ddgzyckx/user/setLocale/en_US?source=/index.php/ddgzyckx/article/view/172009 KVSTER D, HARMS U, 1998. Post-collisional potassic granitoids from the southern and northwestern parts of the late Neoproterozoic East African Orogen: a review[J]. Lithos, 45(1-4): 177-195. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00031-0 LEI T C, CUI F, YU FM, 2012. The application of multi-source information fusion based on remote sensing to ore prospecting prediction in southern Yongzhou of Hunan Province[J]. Geology in China, 39(4): 1069-1080. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI W Y, MA C Q, LIU Y Y, et al., 2012. Discovery of the indosinian aluminum A-type granite in Zhejiang Province and its geological significance[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 55(1): 13-25. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4351-6 LI X, WANG LZ, TU B, et al., 2021. Zircon geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Taibao Pluton in northwest Guangdong Province[J]. Earth Science, 46(4): 1199-1216. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI X F, FENG Z H, XIAO R, et al., 2012. Spatial and temporal distributions and the geological setting of the W-Sn-Mo-Nb-Ta deposits at the northeast Guangxi, South China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(11): 1713-1725. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI X H, LI W X, LI Z X, 2007. On the genetic classification and tectonic implications of the Early Yanshanian granitoids in the Nanling Range, South China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(14): 1873-1885. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0259-0 LI Z J, 2018. Granite in northern Guangxi geochemical characteristics and metallogenic potential analysis[D]. Guilin: Guilin University of Technology: 1-148. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU J C, WANG D Q, ZHANG H D, et al., 2013. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of granite in the Haoyaoerhudong gold deposit in Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 19(4): 413-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU X F, YUAN S D, WU S H, 2012. Re-Os dating of the molybdenite from the Jinchuantang tin-bismuth deposit in Hunan Province and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(1): 39-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Y, LI T D, XIAO Q H, et al., 2010. New chronology of the Ningyuan alkali basalt in southern Hunan, China: evidence from LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(6): 833-841. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Y, LI T D, XIAO Q H, et al., 2012. Formation epoch and origin of the Yizhang andesite, diabase and granite-porphyry in Yizhang County, southern Hu′nan Province: zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopes[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(9): 1363-1378. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Y D, SU X L, CHENG H Y, et al., 2022. Geochronological and geochemical characteristics of the Caledonian Longquan pluton in southern Zhejiang, and their geological significance[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28 (2): 237-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Y Y, 2013. Triassic Shoshonite association: A-type granites belt in South China and its geological implications[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan): 38-80. MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M, 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. GSA Bulletin, 101(5): 635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2 MAO J R, YE H M, LIU K, et al., 2013. The Indosinian collision-extension event between the South China Block and the Palaeo-Pacific plate: evidence from Indosinian alkaline granitic rocks in Dashuang, eastern Zhejiang, South China[J]. Lithos, 172-173: 81-97. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.04.004 MAO J W, XIE G Q, GUO C L, et al., 2007. Large-scale tungsten-tin mineralization in the Nanling region, South China: metallogenic ages and corresponding geodynamic processes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(10): 2329-2338. (in Chinese with English abstract) PEARCE J, 1996. Sources and settings of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes, 19(4): 120-125. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/1996/v19i4/005 PENG S B, JIN Z M, FU J M, et al., 2004. Origin of charnockite and its tectonic significance[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 20(4): 63-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) PENG X J, LIU Y R, LI C H, et al., 2005. The proofs of existing earth crust′s double foundation in the area of Duoponglin-Jiuyan mountainous[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 21(4): 18-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) QIN J F, 2010. Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications of the late-triassic granitoids from the Qinling orogenic belt[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University: 1-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) QING L, JIANG Y H, DU F G, 2020. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of early indosinian A-type granites in the Xinxing Pluton, Southern South China[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 114(3): 217-242, doi: 10.1007/S00710-020-00701-3. SHI Y, SAN Y H, GUO Z C, et al., 2019. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotope compositions of the sillite from Ludong in Fuchuan, northeastern Guangxi[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 39(2): 291-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) SMITH J V, 1974. Feldspar minerals: 2 chemical and textural properties[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer: 1-699. SONG B, ZHANG Y H, WAN Y S, et al., 2002. Mount making and procedure of the SHRIMP dating[J]. Geological Review, 48(S1): 26-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) SU Y P, TANG H F, 2005. Trace element geochemistry of A-type granites[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 24(3): 245-251. (in Chinese with English abstract) SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F, 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 TAO J H, CEN T, LONG W G, et al., 2015. Mineral chemistry of biotites from the Indosinian weakly peraluminous and strongly peraluminous granites in South China and their constraints on petrogenesis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(2): 64-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M, 1985. The continental crust: its composition and evolution: an examination of the geochemical record preserved in sedimentary rocks[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publication. WANG D Z, LIU C S, SHEN W Z, et al, 1993. The contrast between Tonglu Ⅰ-type and Xiangshan S-type Clastoporphyritic lava[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 9(1): 44-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG L J, GRIFFIN W L, YU J H, et al., 2010. Precambrian crustal evolution of the Yangtze Block tracked by detrital zircons from Neoproterozoic sedimentary rocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 177(1-2): 131-144. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2009.11.008 WANG L Y, LIAO Q A, XIAO D, et al., 2016. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of early carboniferous A-type grainte in Harlik, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 22(4): 1032-1048. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG W L, TENG X J, LIU Y, et al., 2017. Zircon U-Pb chronology and geochemical characteristics of the Wuheertu granite mass in Langshan, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 23(3): 382-396. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG X X, WANG T, LU X X, 2001. Studies and problems on rapakivi granites[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 20(4): 19-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Y L, 2014. Early Yanshan granitic magmatic-hydrothermal evolution and tungsten deposits mineralization in Southeast Hunan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing): 1-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W, 1987. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202 WILLIAMS I S, CLAESSON S, 1987. Isotopic evidence for the Precambrian provenance and Caledonian metamorphism of high grade paragneisses from the Seve Nappes, Scandinavian Caledonides: Ⅱ. Ion microprobe zircon U-Th-Pb[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 97(2): 205-217. doi: 10.1007/BF00371240 WILSON M, 1989. Igneous petrogenesis a global tectonic approach[M]. Dordrecht: Springer: 1-466. WU F Y, LI X H, ZHENG Y F, et al., 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185-220. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIANG Y X, WU J H, 2012. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age of Yutian Group basalts in Longnan area of southern Jiangxi Province and its geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(5): 716-725. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIAO D, LIAO Q A, WANG L Y, et al., 2016. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of two types early silurian granites in East Junggar[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 22(4): 1049-1061. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIE G H, 2005. Petrology and geochemistry of Damiao anorthosite and Miyun rapakivi granite-Also on global petrographic anorthosite and rapakivi granitoid[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-195. (in Chinese) XIE H, TIAN J C, ZHANG G L, et al., 2009. A preliminary study on the space distribution regularity of "Increasing distance pattern" of mineralized veins and its structural relation: taking nanzhuhe tin deposit in Dupangling area, South China as an example[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 15(4): 477-484. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU D M, FU J M, CHEN X Q, et al., 2017. Formation age and petrogenesis of the Dupangling rapakivi granites and its geological significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 41(3): 561-576. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU H J, MA C Q, ZHAO J H, et al., 2014. Magma mixing generated triassic I-type granites in South China[J]. The Journal of Geology, 122(3): 329-351. doi: 10.1086/675667 YANG J H, WU F Y, LIU X M, et al., 2005. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes and their geological significance of the Miyun rapakivi granites from Beijing, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(6): 1633-1644. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG L Z, WU X B, HU B, et al., 2018. Geochemistry, geochronology and zircon Hf isotope of Wangxian granodiorite-porphyry in eastern Hunan Province and its geological significance[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 49(9): 2280-2291. (in Chinese with English abstract) YAO Y, CHEN J, LU J J, et al, 2013. Geochronology, Hfisotopic compositions and geochemical characteristics of xitian A-type granite and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 32(3): 467-488. YU J H, ZHOU X M, ZHAO L, et al., 2005. Mantle-crust interaction generating the Wuping granites: evidenced from Sr-Nd-Hf-U-Pb isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3): 651-664. YU J H, WANG L J, WANG X L, et al., 2007. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Fucheng Complex in the southeastern Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(6): 1441-1456. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU J H, O′REILLY S Y, WANG L J, et al., 2010. Components and episodic growth of Precambrian crust in the Cathaysia Block, South China: evidence from U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of zircons in Neoproterozoic sediments[J]. Precambrian Research, 181(1-4): 97-114. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2010.05.016 YUAN S D, LIU X F, WANG X D, et al., 2012. Geological characteristics and 40Ar-39Ar geochronology of the Hongqiling tin deposit in southern Hunan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(12): 3787-3797. (in Chinese with English abstract) YUAN S D, WANG X D, 2013. Zircon LA-(MC)-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and its geological significance of Xianglinpu Pluton in Weijia Tungsten Mine Area, southern Hunan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(S1): 62-64. (in Chinese) ZHANG H F, GAO S, 2012. Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-410. (in Chinese) ZHANG L J, MA C Q, WANG L X, et al., 2011. Discovery of Paleoproterozoic rapakivi granite on the northern margin of the Yangtze block and its geological significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56(3): 306-318. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-4236-7 ZHANG Q, RAN H, LI C D, 2012. A-type granite: what is the essence?[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 31(4): 621-626. ZHAO S R, BIAN Q J, LING Q C, 2004. Crystallography and mineralogy[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press: 1-466. (in Chinese) ZHENG Q R, 1983. Calculation of the Fe3+ and Fe2+contents in silicate and Ti-Fe oxide minerals from epma data[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 3(1): 55-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU B, WANG F Y, SUN Y, et al., 2008. Geochemistry and tectonic affinity of Shanewan orogenic rapakivi from Qinling[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(6): 1261-1272. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU D, HU J, YANG W Q, et al., 2021. Formation age and petrogenesis of the Xinxing pluton in western Guangdong: constraint on the closure of the East Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Geology in China, 48(6): 1896-1923. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU Z X, 1988. Chemical characteristics of mafic mica in intrusive rocks and its geological meaning[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 4(3): 63-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHUAN S P, BAI C D, MAO Z F, et al., 2018. Zircon U-Pb ages and geochemical characteristics of the sugaitilike late silurian granites in Southern Kudi, Xinjiang and its geotectonic significance[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(5): 661-669. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZOU X W, CUI S, QU W J, et al., 2009. Re-Os isotope dating of the Liguifu tungsten-tin polymetallic deposit in Dupangling area, Guangxi[J]. Geology in China, 36(4): 837-844. (in Chinese with English abstract) 柏道远, 陈必河, 钟响, 等, 2014. 湘西南印支期五团岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及形成背景[J]. 中国地质, 41(6): 2002-2018. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.06.015 陈迪, 邵拥军, 刘伟, 等, 2015. 湖南锡田复式花岗岩体岩石学、岩石地球化学特征: 兼对岩石成因类型、岩体侵位机制的探讨[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 31(1): 11-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2015.01.002 陈江峰, 郭新生, 汤加富, 等, 1999. 中国东南地壳增长与Nd同位素模式年龄[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 35(6): 649-658. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ199906000.htm 陈希清, 路远发, 邹先武, 2008. 广西都庞岭、海洋山花岗岩体地球化学特征对比[J]. 地质与勘探, 44(3): 34-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200803008.htm 范蔚茗, 王岳军, 郭锋, 等, 2003. 湘赣地区中生代镁铁质岩浆作用与岩石圈伸展[J]. 地学前缘, 10(3): 159-169. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.015 符金豪, 张建新, 钟坚, 2018. 都庞岭-铜山岭-九嶷山地区区域地球化学空间分带与岩体-地层-成矿作用的关系[J]. 科技通报, 34(5): 35-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJTB201805007.htm 高万里, 王宗秀, 李春麟, 等, 2014. 浙东南印支期花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 88(6): 1055-1067. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201406008.htm 郭锋, 范蔚茗, 林舸, 等, 1997. 湘南道县辉长岩包体的年代学研究及成因探讨[J]. 科学通报, 42(15): 1661-1664. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1997.15.022 何苗, 刘庆, 孙金凤, 等, 2018. 湘东地区锡田印支期花岗岩的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 34(7): 2065-2086. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201807016.htm 贺昕宇, 方同辉, 薄贺天, 等, 2022. 东天山东段国宝山晚二叠世—中三叠世花岗质岩石成因与构造意义: 年代学和地球化学约束[J]. 地质力学学报, 28 (1): 126-142. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222807 侯可军, 李延河, 谢桂青, 2011. LA-MC-ICP MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[M]//李延河. 同位素分析和定年新方法. 北京: 地质出版社: 40-48. 黄海波, 1990. 广西都庞岭花岗岩体基本特征[J]. 中国区域地质, (3): 231-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD199003004.htm 湖南省地质调查院. 2004. 1∶25万湖南道县区域地质调查报告, 1-335. 贾小辉, 王强, 唐功建, 2009. A型花岗岩的研究进展及意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 33(3): 465-480. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.03.017 雷天赐, 崔放, 余凤鸣, 2012. 基于遥感的多源信息融合在湖南永州南部地区找矿预测中的应用[J]. 中国地质, 39(4): 1069-1080. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.04.023 李万友, 马昌前, 刘园园, 等, 2012. 浙江印支期铝质A型花岗岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 42(2): 164-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201202004.htm 李响, 王令占, 涂兵, 等, 2021. 粤西北印支期太保岩体的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 地球科学, 46(4): 1199-1216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202104004.htm 李献华, 李武显, 李正祥, 2007. 再论南岭燕山早期花岗岩的成因类型与构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 52(9): 981-991. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.09.001 李晓峰, 冯佐海, 肖荣, 等, 2012. 桂东北钨锡稀有金属矿床的成矿类型、成矿时代及其地质背景[J]. 地质学报, 86(11): 1713-1725. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.11.001 李镇江, 2018. 广西桂北地区花岗岩的地球化学特征与成矿潜力分析[D]. 桂林: 桂林理工大学: 1-148. 刘建朝, 王得权, 张海东, 等, 2013. 内蒙古浩尧尔忽洞金矿区花岗岩岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 19(4): 413-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2013.04.007 刘晓菲, 袁顺达, 吴胜华, 2012. 湖南金船塘锡铋矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素测年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 28(1): 39-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201201006.htm 刘勇, 李廷栋, 肖庆辉, 等, 2010. 湘南宁远地区碱性玄武岩形成时代的新证据: 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年[J]. 地质通报, 29(6): 833-841. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.06.005 刘勇, 李廷栋, 肖庆辉, 等, 2012. 湘南宜章地区辉绿岩、花岗斑岩、安山岩的形成时代和成因: 锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成[J]. 地质通报, 31(9): 1363-1378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.09.001 刘远栋, 苏小浪, 程海艳, 等, 2022. 浙南加里东期龙泉岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 28 (2): 237-256. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021093 刘园园, 2013. 华南三叠纪橄榄玄粗岩系列: A型花岗岩带及其地质意义[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉): 38-80. 毛景文, 谢桂青, 郭春丽, 等, 2007. 南岭地区大规模钨锡多金属成矿作用: 成矿时限及地球动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 23(10): 2329-2338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.002 彭松柏, 金振民, 付建明, 等, 2004. 紫苏花岗岩成因及构造意义[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 20(4): 63-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2004.04.011 彭学军, 刘耀荣, 李泽泓, 等, 2005. 都庞岭-九嶷山地区早元古代地壳存在证据[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 21(4): 18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2005.04.003 秦江锋, 2010. 秦岭造山带晚三叠世花岗岩类成因机制及深部动力学背景[D]. 西安: 西北大学: 1-282. 时毓, 三元合, 郭智超, 等, 2019. 桂东北富川鲁洞辉绿玢岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素组成[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 39(2): 291-300. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX201902005.htm 宋彪, 张玉海, 万渝生, 等, 2002. 锆石SHRIMP样品靶制作、年龄测定及有关现象讨论[J]. 地质论评, 48(S1): 26-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2002S1006.htm 苏玉平, 唐红峰, 2005. A型花岗岩的微量元素地球化学[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 24(3): 245-251. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2005.03.012 陶继华, 岑涛, 龙文国, 等, 2015. 华南印支期弱过铝质和强过铝质花岗岩中黑云母的矿物化学及其岩石成因制约[J]. 地学前缘, 22(2): 64-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201502007.htm 王德滋, 刘昌实, 沈渭洲, 等, 1993. 桐庐I型和相山S型两类碎斑熔岩对比[J]. 岩石学报, 1993, 9(1): 44-54. 王良玉, 廖群安, 肖典, 等, 2016. 新疆哈尔里克早石炭世A型花岗岩的岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 22(4): 1032-1048. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.04.020 王文龙, 滕学建, 刘洋, 等, 2017. 内蒙古狼山乌和尔图花岗岩岩体锆石U-Pb年代学及地球化学特征[J]. 地质力学学报, 23(3): 382-396. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.03.006 王晓霞, 王涛, 卢欣祥, 2001. 环斑花岗岩研究及存在的问题[J]. 地质科技情报, 20(4): 19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2001.04.004 王艳丽, 2014. 湘东南地区燕山早期花岗岩浆-热液演化及钨矿成矿作用研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京): 1-168. 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等, 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702002.htm 项媛馨, 巫建华, 2012. 赣南龙南地区余田群玄武岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 31(5): 716-725. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.05.008 肖典, 廖群安, 王良玉, 等, 2016. 准噶尔东部早志留世两类花岗岩的岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 22(4): 1049-1061. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.04.021 解广轰, 2005. 大庙斜长岩和密云环斑花岗岩的岩石学和地球化学: 兼论全球岩体型斜长岩和环斑花岗岩类的时空分布及其意义[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-195. 解惠, 田景春, 张桂林, 等, 2009. 矿脉"线性递变不等距"分布规律与构造关系研究: 以广西都庞岭地区南竹河锡矿床为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 15(4): 477-484. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2009.04.006 徐德明, 付建明, 陈希清, 等, 2017. 都庞岭环斑花岗岩的形成时代、成因及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 41(3): 561-576. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201703013.htm 杨进辉, 吴福元, 柳小明, 等, 2005. 北京密云环斑花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 21(6): 1633-1644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200506013.htm 杨立志, 吴湘滨, 胡斌, 等, 2018. 湘东王仙花岗闪长斑岩的岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学和Hf同位素组成[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 49(9): 2280-2291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201809022.htm 姚远, 陈骏, 陆建军, 等, 2013. 湘东锡田A型花岗岩的年代学、Hf同位素、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 32(3): 467-488. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.03.002 于津海, 周新民, 赵蕾, 等, 2005. 壳幔作用导致武平花岗岩形成: Sr-Nd-Hf-U-Pb同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 21(3): 651-664. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200503008.htm 于津海, 王丽娟, 王孝磊, 等, 2007. 赣东南富城杂岩体的地球化学和年代学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 23(6): 1441-1456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.020 袁顺达, 刘晓菲, 王旭东, 等, 2012. 湘南红旗岭锡多金属矿床地质特征及Ar-Ar同位素年代学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 28(12): 3787-3797. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201212001.htm 袁顺达, 王旭东, 2013. 湘南魏家钨矿区祥林铺岩体的锆石LA-(MC)-ICP-MS U-Pb测年及意义[J]. 地质学报, 87(S1): 62-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE2013S1038.htm 张宏飞, 高山, 2012. 地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-410. 张丽娟, 马昌前, 王连训, 等, 2011. 扬子地块北缘古元古代环斑花岗岩的发现及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 56(1): 44-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201101008.htm 张旗, 冉皞, 李承东, 2012. A型花岗岩的实质是什么?[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 31(4): 621-626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2012.04.014 赵珊茸, 边秋娟, 凌其聪, 2004. 结晶学及矿物学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 1-466. 郑巧荣, 1983. 由电子探针分析值计算Fe3+和Fe2+[J]. 矿物学报, 3(1): 55-62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1983.01.009 周滨, 汪方跃, 孙勇, 等, 2008. 秦岭沙河湾造山带型环斑花岗岩地球化学及构造属性讨论[J]. 岩石学报, 24(6): 1261-1272. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200806010.htm 周岱, 胡军, 杨文强, 等, 2021. 粤西新兴岩体的形成时代与成因研究: 对古特提斯洋东支关闭时间的约束[J]. 中国地质, 48(6): 1896-1923. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202106020.htm 周作侠, 1988. 侵入岩的镁铁云母化学成分特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 4(3): 63-73. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1988.03.007 专少鹏, 白春东, 毛志芳, 等, 2018. 新疆库地南苏盖提力克晚志留世花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及大地构造意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 24(5): 661-669. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.05.066 邹先武, 崔森, 屈文俊, 等, 2009. 广西都庞岭李贵福钨锡多金属矿Re-Os同位素定年研究[J]. 中国地质, 36(4): 837-844. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.04.010 -





 下载:
下载: