| Citation: | JIANG Fu-chu, WANG Shu-bin, FU Jian-li, et al., 2006. TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE QINGHAI-TIBET PLATEAU AND ITS CONTIGUOUS AREAS. Journal of Geomechanics, 12 (4): 399-405. |
北斗卫星导航系统(CNSS)是中国自主研制、自行管理的全球卫星定位与通信系统,与美国的全球卫星定位系统(GPS)、俄罗斯的格洛纳斯系统(GLONASS)以及欧盟的伽利略定位系统(Galileo)并称全球四大卫星导航系统。北斗卫星导航系统安全可靠,覆盖范围大,无通信盲区,架设与维护简便,是野外数据传输的理想通信系统[1]。目前北斗卫星导航系统已经广泛应用于地质调查、测绘、交通、海洋渔业、减灾救灾等领域,并产生了显著的经济效益和社会效益。
北斗卫星导航系统是中国自行研制、具有完全自主知识产权的卫星导航系统。北斗卫星导航系统由空间端、地面端和用户端3部分组成。该系统可在全球范围内全天候、全天时为各类用户提供高精度的定位、导航和授时服务,并具备短报文通信能力。
中国此前已成功发射4颗北斗导航试验卫星和13颗北斗导航卫星(其中,北斗-1A已经结束任务),自2011年12月27日,该系统已开始向中国及周边地区提供连续的导航定位和授时服务,后续将在系统组网和试验基础上,逐步扩展为全球卫星导航系统。目前其定位精度优于20 m,授时精度优于100 ns。
北斗卫星导航系统致力于向全球用户提供高质量的定位、导航和授时服务,包括开放服务和授权服务2种方式。开放服务是向全球免费提供定位、测速和授时服务,定位精度10 m,测速精度0.2 m/s,授时精度10 ns。授权服务是为有高精度、高可靠卫星导航需求的用户提供定位、测速、授时和通信服务以及系统完好性信息。
北斗卫星导航系统是中国自主知识产权的卫星导航系统,安全、可靠、稳定,保密性强,适合关键部门应用。它同时具备定位与通讯功能,不需要其他通讯系统支持。数据通信实时性强,传输快捷,一次数据发送时间大约为1 s。
覆盖范围大,无通讯盲区。“北斗一号”卫星导航系统覆盖了中国及周边国家和地区,不仅可为中国、也可为周边国家服务。“北斗”二代将覆盖全球。采用有源定位导航体制,用户终端需要发射入站(返程)信号。
随着“北斗”二代的建设,“北斗”系统发展成为具有全球导航能力的卫星定位系统,定位体制将变为垂直定位,而且随着通信终端性能的逐步提高,通信内容及形式将逐渐丰富,应用的领域也将逐步扩大。
北斗一号卫星系统于2003年建成并投入使用,系统由2颗地球静止卫星(80° E和140° E)、一颗在轨备份卫星(110.5° E)、中心控制系统、标校系统和各类用户机等部分组成。信号覆盖范围为中国领土及周边地区。卫星上行L波段,下行S波段。卫星上设有转发器,可以接收地面站发送的信号,并转发给用户;也可以接收用户请求发送定位信号,并转发给定位总站。
北斗一号卫星系统具有定位功能、授时功能和短报文功能。定位功能具有主动式定位和被动式定位2种,主动式定位在中心站计算;这两种定位都是二维定位,精度为15 m左右。授时功能可以单向授时、双向授时,精度为5~50 ns。短报文功能使用户和中心站之间可进行双向120个字的短报文通信。
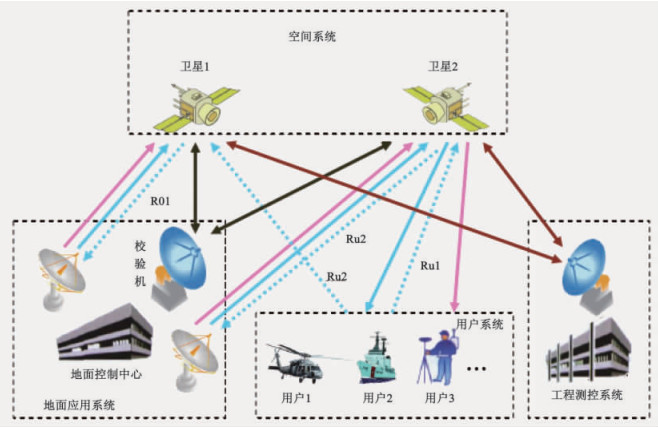
北斗一号卫星系统由空间卫星、地面系统和用户设备等部分组成(见图 1)。

空间卫星部分由2颗对地静止轨道卫星和1颗在轨备份卫星组成,其主要任务是执行地面中心站与用户设备之间的双向无线电信号中继业务。
地面系统部分包括主控站和技术中心(两者合在一起叫地面中心站,配有数字化地形图)、测轨站、气压测高站、校准站等组成设备。
北斗一号卫星系统的用户设备是具有全向收发天线的接收/发送设备,其基本功能一是接收地面中心站通过卫星转发的信号,从中提取信息,并对其进行必要的测量;二是将测量信息或通信信息按一定的时间要求通过卫星发往地面中心站。
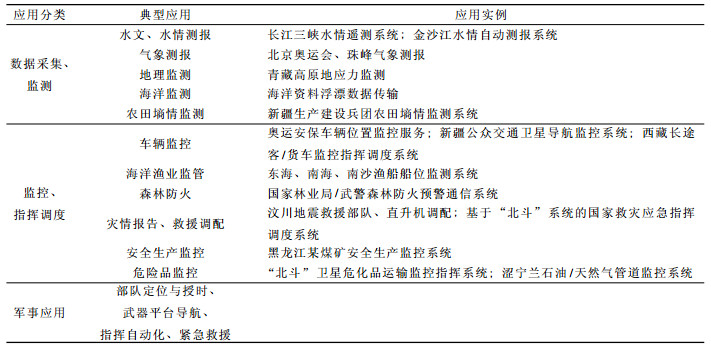
北斗一号卫星系统在中国国防建设和经济社会发展中发挥了积极作用(见表 1),系统目前广泛应用于海洋监测、气象预报、抗震救灾等方面,特别是在汶川抗震救灾中,北斗一号卫星系统为抗震救灾提供了实时的定位、导航、远程监测、灾害预警及公共应急信息服务,发挥了不可替代的作用。
|
总体来说,北斗一号卫星系统的短报文通信功能应用主要集中于数据采集、监测类和监控、指挥调度类;而其实时定位、精确导航及远程监测等功能在抗震救灾和灾害应急救援领域可发挥显著作用。
在应用技术方面,基于北斗一号卫星系统的各种应用大多都集成了地理信息系统(GIS)、北斗/GPS、遥感(RS)、通信(Communication),是“3S+C”的综合应用系统。
北斗二号卫星系统是中国开发的独立的全球卫星定位系统,不是“北斗一号”功能的简单延伸,而更类似于GPS全球定位系统和伽利略系统。第二代北斗导航定位卫星在高度为21500 km的中圆轨道运行,标志着中国自行研制的北斗卫星导航系统进入新的实际应用发展建设阶段。
北斗二号卫星系统的特点如下:① 由区域覆盖(亚太地区)逐渐转向全球覆盖;② 采用类似于GPS、伽利略(Galileo)系统的无源定位导航体制;③ 系统差分定位精度可达1 m;④ 继承“北斗一号”系统的短信报文通信功能,并将扩充通信容量。
中国将在未来几年里陆续发射系列北斗导航卫星,计划2020年前进行系统组网和试验,逐步扩展为全球卫星导航系统。
北斗一号卫星系统对地质调查的安全保障起着重要的应用,目前已初步形成了基于北斗一代卫星的野外地质调查管理与安全保障技术体系。
“十一五”期间,中国地质调查局牵头承担了国家发改委高技术产业化示范工程项目“基于我国卫星的野外地质调查应用高技术产业化示范工程”,研究基于国产遥感卫星和北斗一代卫星的野外地质调查服务与管理应用系统技术体系,形成了一套服务于野外地质调查的“双星野外地质调查服务与管理系统”。通过北斗一代卫星的定位功能满足地质调查领域基于位置的服务需求,利用北斗一代卫星的通讯功能实现野外人员与管理中心之间的实时通讯,保障野外人员的作业安全。系统架构及整体部署见图 2、图 3。
整个系统是一个建立在地调专网环境下的基于网格架构的开放式系统,由6大类节点和外业终端组成,能够实现在双星(遥感卫星和北斗导航卫星)支持下的面向野外地质矿产调查的遥感数据服务和作业管理功能。6大类节点分别为遥感数据服务中心节点、作业管理中心节点、大区中心节点、专业应用中心节点、野外工作站节点及移动驻地节点。
遥感数据服务实现卫星遥感数据快速处理、海量遥感数据库管理和卫星遥感数据服务。作业管理系统一方面能够实现外业人员及单位管理、项目管理、工作组管理、权限管理等相关作业管理功能,另一方面能够实现与外业终端的通信定位、应急救援通讯等功能(见图 4)。作业管理系统是地质调查管理部门实时管理、监测野外工作人员和调配应急装备相互协作的指挥枢纽。
目前,“双星野外地质调查服务与管理系统”已部署在中国国土资源航空物探遥感中心、中国地质调查局发展研究中心、中国地质科学院地质力学研究所、西安地质调查中心、武汉地质调查中心等单位。该系统已在东昆仑、北山、西昆仑等地区进行了实际野外试验,取得了良好的效果。另外,在“3·29飞机失踪事件”第二阶段地面搜索时,搜救人员在天山地区搜救期间配备了北斗终端,既实现了指挥中心实时作业管理,也为搜救人员的人身安全提供了保障。
实践证明,北斗导航系统可以在西部艰险地区稳定工作,为实现野外地质矿产调查工作的生产调度、作业管理及安全保障等提供了技术保证。而随着北斗系统的逐渐完善,及终端研发技术的逐渐发展,北斗系统必将在野外地质矿产调查中发挥更大的作用。
中国地质环境监测院与清华大学合作,针对常见的地面沉降、滑坡等地质灾害,研制了应用于北京、长三角地区、三峡库区、四川等13个地区的基于北斗卫星的地质灾害实时监测系统,建立了能够满足地质灾害实时监测需求的、有效管理各类地质监测信息的综合监测管理系统,实现了监测数据的自动采集、实时传输与存储、快速分析与处理,同时能够管理各类地质灾害监测数据与信息[4~6]。实时监测系统框架见图 5。
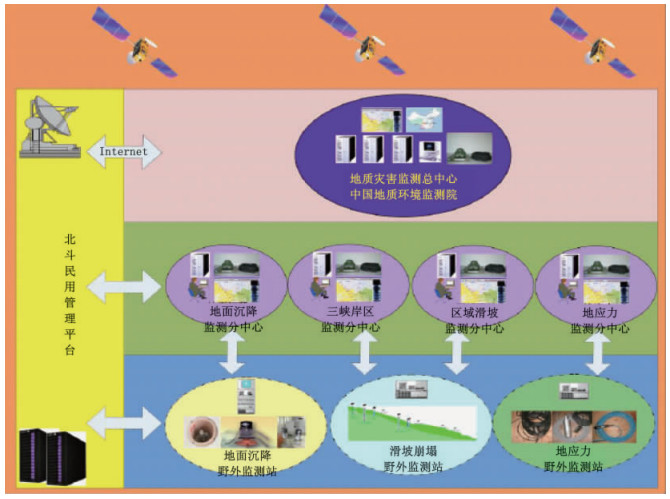
系统分为3层:底层是野外地质灾害监测点,负责自动采集该地的地质灾害监测数据,并将数据通过北斗用户终端发送给所属的地区级分中心;中间层是地区级地质灾害监测分中心,负责监测管辖范围内的地质灾害,并对数据进行分析和处理;顶层是国家级地质灾害监测总中心,利用北斗民用管理平台直接监控各分中心以及各监测点的运行状态,同时获取该系统内各监测点的数据。
北斗卫星系统拥有良好的覆盖性以及监控功能,为地质灾害监测系统提供了通信链路。目前已在示范区建立了4类13个地质灾害监测分中心,实现了对示范区地质灾害的监控和管理。
中国地质环境监测院与清华大学共同研制的基于北斗一号卫星导航系统的滑坡实时监测系统,在四川雅安滑坡地区取得了很好的应用效果。该系统由野外信息采集监测站、数字化滑坡自动监测点、北斗导航卫星通信系统和地质灾害监测分析中心4大部分组成。
北斗卫星滑坡自动化远程监测系统的主要工作流程是:由野外监测站采集地下水位、降雨量、水温、地表位移、深部变形等地质环境特征数据,根据需要定时操控或由远程遥控,利用北斗卫星导航系统将数据直接发送至地质灾害监测中心,由监测中心对数据进行分析处理,同时可通过北斗系统向野外系统发送反馈信息和控制指令。
基于北斗卫星的滑坡实时监测系统是一套实时、远程控制的自动化监控系统,该系统可以在传统通讯手段使用不便的地区,利用北斗卫星系统及时、准确、方便地获取各个滑坡危险地区实时监测数据,对今后滑坡灾害的调查分析和预报具有重要的意义。
中国地质科学院地质力学研究所与清华大学合作开发了基于北斗一号卫星导航系统的青藏高原地应力实时监测系统。该系统由中心站控制处理单元、北斗一号卫星通信单元和野外数据采集单元组成[7]。系统的基本结构如图 6所示。
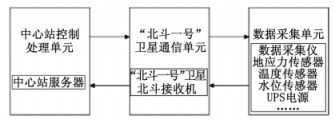
该系统开发完成后,在西藏曲水、林芝两地建立了2个野外监测站,在北京地质力学研究所建立了中心站。实际运行情况表明,北斗一号导航卫星系统在青藏高原地应力实时监测的应用是成功而有效的,该系统的建立为北斗一号导航卫星系统在相关领域的应用以及地质灾害监测数据的远程传输提供了借鉴经验。
在“5.12”汶川地震后的抗震救灾工作中,北斗卫星导航系统发挥了重要的作用,保障了抗震救灾与应急指挥的顺利进行,充分体现了北斗导航定位系统在抗震救灾应用中的不可替代性[8~9]。北斗卫星导航系统在“5.12”抗震救灾中的应用主要有:① 为“5.12”抗震救灾的救援直升机提供了导航定位;② 在地震造成通讯中断、道路损毁的情况下为抗震救灾提供可靠的通信保障,为灾区一线和指挥部建立了实时通信通道,把灾区的实时情况及时传回指挥部,在决策、搜救、医疗等过程中发挥了关键作用,为取得5.12抗震救灾的伟大胜利奠定了决定性的基础;③ 为减灾防灾提供远程监测和灾情预警;④ 为社会大众提供公共应急信息服务。
中国地质环境监测院与清华大学合作,以北斗卫星导航系统为平台,集计算机技术、测绘技术、卫星导航定位技术、通信和图像传输等技术于地理信息系统,在掌上PDA实现抗震救灾分队与指挥部信息共享,建立了抗震救灾应急指挥系统[6, 10]。通过北斗卫星可以为抗震救灾提供导航、定位及实时灾情上报,协助抗震人员实施各种抗震救灾行动,从而大大提高抗震救灾能力,最大限度地减少地震带来的财产损失和人员伤亡。用PDA实时将灾区信息标绘在电子地图上并迅速发送到指挥部,及时提供准确的灾区信息,为抗震救灾决策提供了科学依据,为夺取抗震救灾决定性胜利提供可靠的技术保障。
抗震救灾应急指挥系统主要包括灾情信息采集和灾情信息发布2个子系统。灾情信息采集子系统按照其功能可分为导航监控、指挥管理、辅助决策、数据分发模块;灾情信息发布子系统包括了导航定位、应急标绘、应急信息发布模块,两个子系统均以GIS管理和网络通信为支撑(见图 7)。
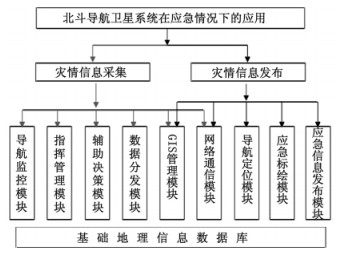
实际应用中灾情核查人员将附有定位信息的灾情信息通过北斗卫星以短信方式传输给应急指挥中心,指挥中心将信息和数据及时汇总,并通过GIS技术将灾情信息整合到电子地图上,从而迅速开展灾情评估工作。
北斗卫星导航系统良好的导航定位功能,可以为灾区的现场工作组和救援人员提供实时的定位服务,尤其是在边远山区,可以为灾情信息采集提供高效、实时的技术保障,以便及时制定应对措施。
首先,目前地质行业普遍应用的卫星导航系统是美国的全球定位系统(GPS),其数据安全保密性得不到保障。从国家长远战略角度考虑,作为国家重要的行业,其信息数据受制于国外,存在极大的安全隐患。北斗卫星系统是中国自主知识产权的卫星导航系统,安全、可靠、稳定、保密性强,非常适合地质领域的应用。
其次,在地质调查、矿山监测、地质灾害调查等很多涉及野外工作的领域,坐标信息是非常重要的。没有坐标信息,其他的地质资料就没有依附介质,也就无法为实际找矿提出依据。而在相应的野外工作中,坐标信息的获取则更是必不可少的环节。区域地质调查工作中,使用的GPS定位精度只需满足图幅1 mm的误差即可。而遥感地质调查工作中,不仅需要对采样点、观测点及异常点采集定位坐标信息,更主要的还需要采集控制点的定位坐标信息用于图像的几何校正、镶嵌融合。根据中国地质调查局地质调查技术标准中的《遥感影像地图制作规范》规定,误差不能大于1个像元。北斗二号卫星导航系统具有精确定位(差分定位精度达到1 m),完全可以满足面向国土资源调查监测的基于位置服务的精度要求。
第三,在野外地质调查工作中,需要将实地获取的坐标信息及时回传给管理部门,一方面实时更新相关数据,另一方面便于野外作业管理。而目前国际上通用的几种卫星导航系统都采用无源定位方式,这种定位方式下定位人员只能自己看到定位信息,而无法使其他人获知。因此,通常通过Internet网络、GPRS或3G网的方式传至管理中心。在一些偏远地区,没有互联网、基站等设施时,则无法实现数据的回传。而在国土资源行业,在这样偏远地区的业务工作不在少数。北斗系统独有的短信通讯功能可以向有关方面传达信息,实现互联互通,使管理部门实时了解野外地质调查工作态势,并在应急情况下向野外作业人员提供实时援助,保障野外作业人员的安全。
第四,在艰险地区进行野外工作的外业人员,由于实地地理环境复杂、人烟稀少、手机信号覆盖差等情况,其野外作业安全问题一直较为突出。尽管主管部门出台了一系列措施并配备了电台、海事卫星电话等设备加强野外工作安全,但艰险地区事故发生率依然很高。其主要原因在于没有较为低廉轻便的通信设备进行日常的安全管理。随着国产北斗卫星导航技术的发展,近年来,北斗一代卫星在地质调查领域有了广泛的应用,初步形成了基于北斗一代卫星的野外地质调查管理与安全保障技术体系[11~12]。主要是使用北斗一代卫星的定位功能实现地质调查领域的基于位置的服务需求,使用北斗一代卫星的通讯功能实现野外人员与管理中心之间的实时通讯,保障野外人员的作业安全。“十一五”期间,中国地质调查局启动了北斗一代卫星在地质调查领域的应用示范项目,这为艰险地区的野外工作安全保障提供了又一条可行之路。
北斗卫星导航系统是中国具有自主产权的卫星导航系统,既有导航定位功能,又有短报文通信功能。北斗系统已经广泛应用到中国野外地质调查、地质灾害监测等领域,为地质调查安全保障、地质灾害实时监测、灾害信息采集和应急指挥提供了有力的技术支撑手段,尤其在中国偏远、地形复杂、通信不畅的地区使用更具有明显的优势。
随着北斗二代卫星系统的建设,北斗卫星导航系统将成为全球覆盖、高精度、无通讯盲区的导航系统,在国家卫星导航科技专项和相关政策推动下,北斗卫星导航系统将在地质调查领域发挥更加重要和不可替代的作用。
