| Citation: | ZHANG Chun-shan, ZHAN Li-hai, WU Man-lu, et al., 2004. SEISMIC DANGER DIVISIONS BASED ON HYDROGEOCHEMICAL-TECTONIC CHARACTERISTICS ON THE CONTINENT OF CHINA. Journal of Geomechanics, 10 (3): 213-226. |
断裂作用可导致两种不同形式应变:连续应变和非连续应变。由断裂位移来估算的应变是非连续应变[1~3] (图 1)。由于应变概念只能应用于连续变形, 所以Jamison (1989) [1]引进了断裂应变这一词, 用来描述由一系列断裂位移导致的非连续变形。实际上, 断裂应变是非连续应变还是连续变形取决于所研究的范围和断裂位移的相对大小[1, 4]。如果所研究地区的尺度与断裂位移相比大很多, 断裂应变就可以视为连续变形。到目前为止, 断裂应变在构造地质界尤其在中国构造地质界没有得到足够重视。这主要是由于计算断裂应变必须获得每一条断裂位移大小和方向。这在野外工作中是比较困难的。因为往往缺乏合适的和足够的被错动标志体。但是对于露头条件很好的地区, 尤其是现代断裂活动区, 比较而言容易观察到断裂运动标志体。这些标志物很少经过后期的破坏和沉积物覆盖。
对于断裂应变, 有两种计算方法。一种是计算单个断裂引起的应变量, 也就是垂直断裂方向的剖面上求水平方向的应变。另一种通过研究区内所有断裂数据求断裂应变椭球体, 这样就可以知道主应变的方向和大小。本文只介绍第一种方法。
变形实验表明, 在断裂发生前, 有一定的弹性应变积累。在静岩应力条件下(σv=σH=σh=ρgz), 其表达式为:
|
|
(1) |
这里εh为静岩应力条件下的水平应变, E是扬氏模量, ν为泊松比, ρgz就是垂直应力。如果岩体变形已经达到断裂阶段, 这种弹性应变已不可恢复。但是它与断裂引起的塑性应变相比通常可以忽略不计。
断裂作用过程中, 并不总是断块的刚性运动, 而是可以引起地块一定的塑性变形。这种塑性应变与断裂最大位移量和断裂长度有关。Schultz和Fossen (2002) [5]给出了一个计算公式:
|
|
(2) |
这里D为断裂最大位移, L为断裂长度, δ为断裂倾角, 而σ为断裂面上有效应力的校正值, 其具体的计算表达式见Schultz和Fossen (2002) [5]。
据Schultz和Fossen (2002), 对于正断层, 计算出的伸展应变为2 %~ 3 %; 对于逆断层, 计算出的压缩应变为4 %~ 5 %。如图 2所示, 这种应变与断裂最大位移(D)与断裂长度(L)的比值成正相关。即比值越大, 应变量越大。
断裂应变与三个因素有关:断裂几何形态、断裂的旋转性、断裂的位移大小。这三种因素的不同组合, 给出的计算方法不一样。断裂有很多的分类方法, 在这里不一一列举。我们只介绍Wernicke (1982) [6]的分类方法。他是根据断裂形态和断裂旋转性来进行分类的(表 1)。按照这个分类, 只有平面状断裂不会引起地层旋转情况。铲状断裂可以引起地层旋转但本身不一定旋转。如果同时有地层和断裂旋转, 可以是平面状断裂也可以铲状断裂引起。
到目前为止, 已提出了三种断裂旋转机制。最早认为, 断裂旋转是刚性的, 断块内部没有任何变形[7]。这种机制存在的问题是断裂旋转产生的空隙, 这些空隙没有用其他的机制加以完满解释。而且这种空隙与旋转幅度成正比(图 3)。由于上述原因产生了垂直简单剪切和斜向简单剪切模型。垂直剪切机制提出断裂上盘由于断裂作用, 发生垂直方向的简单剪切作用。越靠近断裂, 剪切作用越强, 同时认为这种剪切机制也是地层旋转的原因[8~10]。然而有作者认为, 在铲状断裂的上盘, 剪切方向不一定是垂直的, 它可以在任何方向进行, 这取决于断裂的几何形态和远场应力作用状态。这就是所谓的斜向简单剪切机制[11] (图 4)。
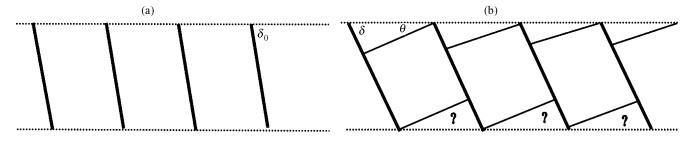
当断裂和地层都不发生旋转时(δ =δ0), 断裂作用前后地层的长度不变(图 5)。断裂引起的伸长CB (对正断层而言)或缩短(对逆断层而言)等于断裂水平断距或平错。因为CB等于dcos (δ), 所以应变量应为:
|
|
(3) |
从(3)式可以看到, 应变的大小与断裂倾角成反相关关系; 也就是说, 对相同的总位移, 断裂倾角越大, 应变越小。同时也能看到, 应变与位移大小成正相关关系; 也就是说, 相同的断裂倾角, 总位移越大, 应变越大。
对于刚性旋转机制断块(图 6), 由于在断块内部没有变形, 断裂旋转的角度等于地层的倾角, 即θ=δ0-δ。断裂的平错等于L0cot(δ)sin(θ), 断裂作用后的长度为D′C′=D′B+BC′=L0[cot(δ)sin(θ)+cos(θ)], 所以应变大小为:
|
|
(4) |
由(4)式可以看到, 应变大小与断裂现在的倾角δ和地层的倾角θ有着很复杂的关系, 而不是我们想象的那么简单。特别地, 我们由断裂现在的倾角δ可以计算断裂形成时的倾角δ0, 其表达式是:
|
|
(5) |
对于垂直剪切机制, 断块内部发生了垂直方向简单剪切。这样一来, 断块旋转以后的地层长度比原来的要长, 但在水平方向的投影与原始的长度一致。如图 7所示, 断裂平错为h =Lbcot(δ)sin(θ), 变形前的长为L0=Lbcos(θ), 所以应变大小为:
|
|
(6) |
由(6)式可以推断, 应变大小与断裂现在的倾角成反相关关系, 而与地层的倾角成正相关关系。有兴趣的读者可以计算一下, 对于相同的断裂旋转角, 垂直剪切引起的水平应变要大于刚性旋转引起的应变量[10]。
同样地, 由断裂现在的倾角δ可以计算断裂形成时的倾角δ0, 其表达式是:
|
|
(7) |
可以看到, 对于垂直剪切机制, 变形前后的断裂倾角不是简单的代数关系。比较式(7)和式(5), 对于相同的地层倾角和断裂现在的倾角, 由垂直剪切机制得到的断裂原始倾角相对较小。
斜向剪切机制与垂直剪切机制有些类似(图 8)。但是二者相比, 斜向剪切机制引起的拉伸量比垂直剪切机制引起的拉伸量大, 用等式表示为:
|
|
(8) |
其应变量为:
|
|
(9) |
从这个方程可以推断, 当α等于零时, 式(9)等同于式(6)。式(9)可以进一步变为:
|
|
(10) |
该式表明, 只要tan(α)tan(θ)小于1, 斜向剪切机制引起的拉伸量比垂直剪切机制引起的拉伸量大。据White等(1986)[11], α的大小一般小于45度, θ的大小也小于45度, 因此, tan(α)tan(θ)小于1。
我们考察来自于墨西哥中央桌子山San Miguelito地区渐新世火山岩区的断裂。该区发育有一系列的多米诺式的正断层(图 9)。通过研究认为, 这些断裂经历了垂直剪切作用。
断裂参数都是通过野外质地测量所得(表 2)。测量标志体为Cantera未熔结凝灰岩。地层倾角为断块内的平均值。也就是通过测量一系列的倾角值, 然后求得平均值。在一个断块内, 可以得到5~10个地层数据。我们看到, 每一断块的应变量各不相同。各断块的地层的拉伸应变的最大值15. 5 % (断块7), 而水平应变的最大值达31. 2 % (断块8)。对于整个剖面, 求得的应变量为20 %。
(1) 断裂作用可导致连续应变即塑性变形与非连续应变。他们分别有不同的计算公式。
(2) 计算断裂的非连续应变应考虑断裂几何形态、断裂的旋转与否、断裂的位移大小等三个因素。
(3) 刚性旋转时, 没有断块内变形。它引起的水平非连续应变最小。垂直剪切作用使断块内地层变形, 即有地层的连续性应变。在相同条件下, 它引起的非连续应变量比刚性旋转机制引起的非连续应变量大。斜向剪切也使断块内地层变形, 也有地层的连续性应变。在相同条件下, 它引起的非连续应变比垂直剪切机制引起的非连续应变应变大。
