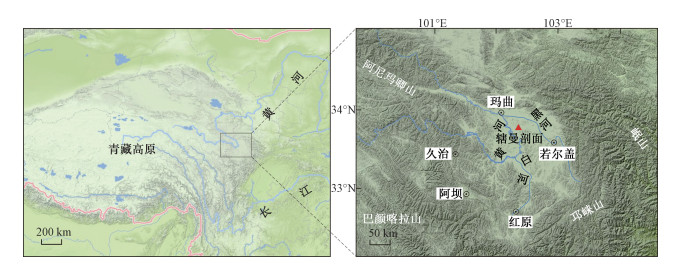
Paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental evolution recorded by the aeolian sand-paleosol sequence in the Zoigê basin
-
摘要: 通过对若尔盖盆地中部辖曼地区风成砂-古土壤沉积序列的粒度分析、孢粉鉴定、磁化率测定以及AMS 14C年代测定,探讨了该地区末次冰消期以来古气候与古环境的演化过程。研究结果表明,若尔盖地区的土地沙化现象至少在距今16 ka余年的末次冰消期就已经出现。地层结构、粒度、磁化率皆指示该区古气候在末次冰消期以来经历了多次冷暖交替变化,沙地也经历了多次的固定与活化过程,其中16130~6460 aB.P.、3445 aB.P.前后以及700 aB.P.前后气候较为温暖湿润,在8170~6460 aB.P.期间有一次极暖事件。自11.3 kaB.P.开始,古土壤中的喜暖型乔木花粉含量明显降低,草本植物、尤其是狐尾藻属和莎草科等沼泽植物孢粉含量明显增多,指示该区古环境发生明显变化,开始发育沼泽泥炭。Abstract: The aeolian sand-paleosol sequence in the Zoigê basin is a sensitive record of paleoclimate change and paleoenvironmental evolution for the northeastern region in the Tibet Plateau. A typical aeolian sand-paleosol section, called Xiaman, was tested for its AMS C age, grain size, magnetic susceptibility and sporo-pollen. Then the paleoclimate and paleoenvironment evolution since the last deglacial period in this area was discussed. The results show that the land desertification in the Zoigê basin occurred at least in the last deglacial period of more than 16 ka years ago. Variations of the formation structure, grain size and magnetic susceptibility indicate that the paleoclimate has undergone many alternations of cold and warm, and the sandy land has also experienced many processes of fixation and activation. The climate tended to be relatively warm and wet during 16130~6460 aB.P., around 3445 aB.P. and 700 aB.P.. There was a very warm period during 8170~6460 aB.P.. Since 11.3 kaB.P., the sporo-pollen contents of warm-fitted trees in paleosol have decreased considerably, while that of herbaceous plants, especially swampy plants, such as Myriophyllum and Syperaceae, have increased obviously, indicating that the paleoenvironment has significantly changed and the swampy peats have begun to develop.
-
Key words:
- Zoigê basin /
- last deglacial period /
- aeolian sand /
- environmental evolution /
- land desertification
-
表 1 辖曼剖面AMS 14C测年数据和校正年龄
Table 1. AMS 14C dating and calibration results of the samples from the Xiaman section
样品号 深度/cm 层位 测试材料 14C年龄/aB.P. 校正年龄/cal.aB.P. XM1 70 2 全碳 735±40 700 XM2 315 4 全碳 3165±40 3445 XM3 495 6 全碳 5695±120 6460 XM4 505 6 全碳 7355±180 8170 XM5 555 6 全碳 13430±210 16130 -
CAI M T, YE P S, YANG X C, et al., 2018. Evolution of sedimentary environment in the North Hetao Basin since 344 Ka[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(2):253-262. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201802013 CAI Y, 2008. Study on environmental change in Zoigê plateau: evidence from the vegetation record since 24, 000 aB.P.[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN S Y, WANG S M, 2002. Environmental changes and its responding to tectonic uplift of Tibetan Plateau during the last 2.8 Ma recorded by lake sediments[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 8(4):333-340. (in Chinese with English abstract) CLARK P U, DYKE A S, SHAKUN J D, et al., 2009. The last glacial maximum[J]. Science, 325(5941):710-714. doi: 10.1126/science.1172873 DING Z L, SUN J M, LIU D S, 1999. Stepwise advance of the Mu Us Desert since late Pliocene:evidence from a red clay-loess record[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44(13):1211-1214. doi: 10.1007/BF02885968 HERZSCHUH U, BIRKS H J B, LIU X Q, et al., 2010. What caused the mid-Holocene forest decline on the eastern Tibet-Qinghai Plateau?[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19(2):278-286. HU G Y, JIN H J, DONG Z B, et al., 2013. Driving forces of aeolian desertification in the source region of the Yellow River:1975-2005[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 70(7):3245-3254. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2389-9 LI B, DONG S C, JIANG X B, et al., 2008. Analysis on the driving factors of grassland desertification in Zoige wetland[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 15(3):112-115, 120. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stbcyj200803029 LI F R, ZHAO Y, SUN J H, et al., 2011. Surface pollen and its relationship to vegetation in the Zoige Basin, eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 5(3):252-261. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zggdxxxswz-dqkx201103004 LI H, 2015. Holocene pollen record and reconstruction of palaeovegetation and palaeoclimate in the Zoige Basin, Tibetan Plateau[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI M Q, JIN H L, ZHANG H, et al., 2005. Climate change revealed by magnetic susceptibility and organic matter during the Holocene in Hunshandak desert[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 23(4):683-689. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200504018 LI Z W, LI B S, SUN L, et al., 2008. Evolution of multifactors that affect the susceptibility of China's loess[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 28(2):231-237. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU G X, SHEN Y P, WANG R, et al., 1995. The vegetation and climatic changes in Zoige during the last 20 000 years determined by pollen records[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 17(2):132-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500163251 LIU X M, LIU T S, HELLER F, et al., 1992. Study on magnetic susceptibility of loess and Quaternary climate in China[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 27(A1):279-285. (in Chinese with English abstract) LU H Y, AN Z S, 1998. Paleoclimatic significance of grain size of loess-palaeosol deposit in Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 41(6):626-631. doi: 10.1007/BF02878745 SHEN C M, LIU K B, TANG L Y, et al., 2006. Quantitative relationships between modern pollen rain and climate in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 140(1-2):61-77. doi: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2006.03.001 SHENG H Y, WANG Y J, 2007. Grassland desertification and controlling measures in the Ruoergai plateau[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 27(1):126-131, 158. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stbctb200701031 SUN G Y, LUO X Z, TURNER R E, 2001. A study on peat deposition chronology of Holocene of Zorge plateau in the northeast Qinghai-Tibetan plateau[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 19(2):177-181, 206. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200102003 SUN J M, DING Z L, 1995. Preliminary studying on the physical mechanism of magnetic susceptibility of Chinese loess[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 10(4):88-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) SUN J M, LI S H, HAN P, et al., 2006. Holocene environmental changes in the central Inner Mongolia, based on single-aliquot-quartz optical dating and multi-proxy study of dune sands[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 233(1-2):51-62. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031018205005493 SUN X H, ZHAO Y, LI Q, 2017. Holocene peatland development and vegetation changes in the Zoige Basin, eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 60(10):1826-1837. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9086-5 WANG F B, YAN G, HAN H Y, et al., 1996. Paleovegetational and paleoclimatic evolution series on northeastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in the last 30 ka[J]. Science in China Series D-Earth Sciences, 39(6):640-649. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e3fca8a382ad1c856f096fee68b0187a WANG M H, 1987. The spore-pollen groups of peatland on Ruoergai plateau and paleobotany and paleoclimate[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 7(2):147-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG X F, HE P, KANG W X, 2014. Dynamic characteristics of land desertification status quo and desertification development in Ruoergai County, Sichuan province[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 34(12):124-129. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/znlxyxb201412023 WANG Y F, WANG S M, XUE B, et al., 1995. Sedimentological evidence of the piracy of fossil Zoige Lake by the Yellow River[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 40(18):1539-1544. WANG Y, ZHAO Z Z, QIAO Y S, et al., 2005. Characteristics of the climatic variatation in Zoigê in the past 45 years and its effects on the eco-environment in the area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 11(4):328-332, 340. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Y, ZHAO Z Z, QIAO Y S, et al., 2006. Paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental evolution since the late glacial epoch as recorded by sporopollen from the Hongyuan peat section on the Zoige plateau, northern Sichuan, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(7):827-832. (in Chinese with English abstract) XUE B, WANG S M, WU J L, et al., 1999. Palaeoclimate of northeastern Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) plateau since last interglaciation:A case study from core RM of the Zoige basin[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 30(3):327-332. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU X F, ZHOU W J, FRANZEN L G, et al., 2006. High-resolution peat records for Holocene monsoon history in the eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science in China Series D, 49(6):615-621. doi: 10.1007/s11430-006-0615-y ZHAN T, ZENG F M, XIE Y Y, et al., 2018. Grain size characteristics of Tianhengshan core and their indications for stratigraphic division in the eastern part of the northeast plain of China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(4):515-521. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201804009 ZHANG S Q, GUO H Y, QING Q T, et al., 2006. Study on the MODIS remote sensing of the grassland desertification in Ruoerge plateau and its driving force[C]//Proceeding of the annual conference of the Chinese meteorological society. Chengdu: Chinese Meteorological Society: 1077-1085. (in Chinese) ZHANG W L, 2015. The desertification evolution reflected by grain-size and magnatic susceptibility in Maqu plateau since Middle-late Holocene[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU W J, LU X F, WU Z K, et al., 2002. Peat record reflecting Holocene climatic change in the Zoige Plateau and AMS radiocarbon dating[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(1):66-70. doi: 10.1360/02tb9013 蔡茂堂, 叶培盛, 杨星辰, 等, 2018.河套盆地北部344 ka以来沉积环境演化[J].地质力学学报, 24(2):253-262. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180212&flag=1 蔡遥, 2008.若尔盖地区24000年以来植被记录的环境变化研究[D].北京: 中国地质科学院. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-2008177408.htm 陈诗越, 王苏民, 2002.青藏高原2.8 Ma来的环境演化及其对构造事件响应[J].地质力学学报, 8(4):333-340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2002.04.007 丁仲礼, 孙继敏, 刘东生, 1999.上新世以来毛乌素沙地阶段性扩张的黄土-红粘土沉积证据[J].科学通报, 44(3):324-326. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.03.022 李斌, 董锁成, 江晓波, 等, 2008.若尔盖湿地草原沙化驱动因素分析[J].水土保持研究, 15(3):112-115, 120. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stbcyj200803029 李焕, 2015.青藏高原若尔盖泥炭地孢粉记录的全新世以来植被和环境变化[D].兰州: 兰州大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10730-1015352322.htm 李明启, 靳鹤龄, 张洪, 等, 2005.浑善达克沙地磁化率和有机质揭示的全新世气候变化[J].沉积学报, 23(4):683-689. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.04.018 李志文, 李保生, 孙丽, 等, 2008.影响中国黄土磁化率差异的多因素评述[J].中国沙漠, 28(2):231-237. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsm200802008 刘光锈, 沈永平, 王睿, 等, 1995.孢粉记录揭示的2万年以来若尔盖地区的气候变化[J].冰川冻土, 17(2):132-137. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500163251 刘秀铭, 刘东生, HELLER F, 等, 1992.中国黄土磁化率与第四纪古气候研究[J].地质科学, 27(A1):279-285. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKX1992S1026.htm 盛海洋, 王玉珏, 2007.若尔盖高原沙漠化成因及其治理对策[J].水土保持通报, 27(1):126-131, 158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2007.01.031 孙广友, 罗新正, TURNER R E, 2001.青藏东北部若尔盖高原全新世泥炭沉积年代学研究[J].沉积学报, 19(2):177-181, 206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.02.003 孙继敏, 丁仲礼, 1995.浅议中国黄土磁化率的物理意义[J].地球物理学进展, 10(4):88-93. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWJ504.007.htm 王曼华, 1987.若尔盖高原区泥炭地的孢粉组合及古植被与古气候[J].地理科学, 7(2):147-155. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DLKX198702005.htm 汪晓菲, 何平, 康文星, 2014.若尔盖县土地沙化现状及沙化发展动态特征[J].中南林业科技大学学报, 34(12):124-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2014.12.023 王燕, 赵志中, 乔彦松, 等, 2005.若尔盖45年来的气候变化特征及其对当地生态环境的影响[J].地质力学学报, 11(4):328-332, 340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2005.04.005 王燕, 赵志中, 乔彦松, 等, 2006.川北若尔盖高原红原泥炭剖面孢粉记录的晚冰期以来古气候古环境的演变[J].地质通报, 25(7):827-832. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.07.009 薛滨, 王苏民, 吴敬禄, 等, 1999.青藏高原东北部末次间冰期以来的古气候:以若尔盖盆地RM孔分析为例[J].海洋与湖沼, 30(3):327-332. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1999.03.017 詹涛, 曾方明, 谢远云, 等, 2018.东北平原东部天恒山钻孔的粒度特征及其对地层划分的指示[J].地质力学学报, 24(4):515-521. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180409&flag=1 张顺谦, 郭海燕, 卿清涛, 等, 2006.若尔盖高原草地沙化的MODIS遥感及其驱动力研究[C]//中国气象学会2006年年会"气候变化及其机理和模拟"分会场论文集.成都: 中国气象学会: 1077-1085. 张文丽, 2015.粒度和磁化率反映的中晚全新世以来玛曲高原的沙漠化演化[D].兰州: 西北师范大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10736-1015654002.htm -





 下载:
下载: