MINERAL COMPOSITION AND PLATINUM-GROUP ELEMENTS OF THE NEOPROTEROZOIC WANGJIANGSHAN LAYERED INTRUSION AT THE NORTHERN MARGIN OF THE YANGTZE BLOCK: IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROCESSES OF MAGMA EVOLUTION AND TECTONIC SETTING
-
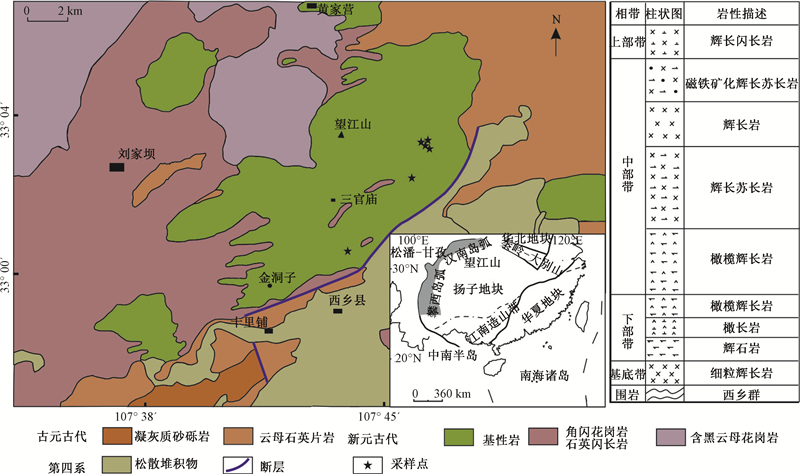
摘要: 望江山层状岩体位于扬子地块北缘新元古代汉南杂岩带中,岩体从底部到顶部由超镁铁质岩过渡为中性岩:底部主要由辉石岩和橄长岩组成;中部为辉长苏长岩和辉长岩;上部为辉长岩和闪长岩。研究以中部岩相带橄榄辉长苏长岩、辉长苏长岩和辉长岩为对象,通过主要矿物的主微量元素和全岩主微量元素的分析,查明望江山岩体来源于尖晶石二辉橄榄岩组成的大陆下岩石圈地幔,并且地幔源区受到了来自俯冲板片流体的交代,岩体中部带的母岩浆为拉斑玄武质岩浆。钛铁矿—磁铁矿矿物对成分计算表明,母岩浆在形成时具有较高氧逸度。通过单斜辉石压力计得到岩体的侵位深度约为12.9~18 km。对岩体母岩浆橄榄石分离结晶过程的模拟计算表明,中部带橄榄石为母岩浆经过~28%分离结晶的产物。此外,铂族元素(PGE)组成暗示岩体并未经历过大规模的硫化物熔离,可能与缺乏地壳物质混染有关。岩体中单斜辉石与岛弧环境堆晶岩中单斜辉石成分相似,不同于裂谷环境中堆晶单斜辉石的成分;同时,全岩Th/Yb和Nb/Yb比值也与岛弧玄武岩比值相似,因此矿物和全岩成分均说明望江山层状岩体应形成于岛弧环境。研究认为扬子北缘在新元古代长期的俯冲过程中,大洋板片断离导致软流圈上涌,提供热源使交代大陆下岩石圈地幔部分熔融形成具有岛弧特征的镁铁质岩浆,在局部伸展环境中上升侵位形成汉南杂岩带中镁铁—超镁铁质层状岩体。Abstract: The Wangjiangshan layered intrusion occurs in the Neoproterozoic Hannan arc at the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, and it is composed of ultramafic to intermediate rocks from the bottom to the top. The lower zone is mainly composed of pyroxenite and troctolite, the middle zone is olivine gabbro and gabbro, and the upper zone is gabbro and diorite. This study focuses on olivine noritegabbro, noritegabbro and gabbro in the middle zone. The compositions of olivine, pyroxene and bulk-rock suggest that the Wangjiangshan intrusion was derived from subcontinental lithospheric mantle which was mainly composed of spinel lherzolite and metasomatized by subducted slab-derived fluids. The parental magma of the middle zone was tholeiitic basalt with high oxygen fugacity, inferring from the in-situ compositions of ilmenite-magnetite mineral pair. The shallow magma chamber was about 12.9 to 18 km in depth in terms of clinopyroxene geobarometry. The modeling result shows that olivine from the middle zone was a product of~28% crystallization of the parental magma. In addition, the PGE pattern of the rocks from this study indicates a lack of large-scale sulfide segregation due to the absence of crustal contamination. The composition of clinopyroxene is akin to those from island arc, but different from clinopyroxene from the rifting. Moreover, rocks from the middle zone have bulk-rock Th/Yb and Nb/Yb ratios similar to ratios of island arc basalts. Therefore, the Wangjiangshan intrusion could be formed in island arc environment. We argue that the tearing and breakoff of subduction oceanic slab resulted in asthenosphere upwelling during the Neoproterozoic long-term subduction beneath the northern margin of Yangtze. This provided a heat source for the partial melting of the metasomatized subcontinental lithospheric mantle and subsequent formation of mafic magma with island arc characteristics, which ascended in an extensional environment to form mafic-ultramafic layered intrusions in the Hannan arc.
-
图 2 望江山岩体中不同岩石类型的岩相学特征
a—橄榄辉长苏长岩,单斜辉石(Cpx)、斜方辉石(Opx)和斜长石(Pl)自形程度接近形成辉长结构,正交偏光,样品WJS-21;
b—橄榄辉长苏长岩,橄榄石(Ol)被次生的角闪石(Amp)所包裹,正交偏光,样品WJS-20;
c—辉长岩,铁钛氧化物分布在硅酸盐矿物粒间,正交偏光,样品WJS-4;
d—辉长苏长岩,斜长石(Pl)、斜方辉石(Opx)和单斜辉石(Cpx)均呈半自形等轴粒状,辉长结构,正交偏光,样品WJS-34Figure 2. Petrographic characteristics of different rock types from the Wangjiangshan intrusion
图 9 望江山岩体地幔源区性质判别图
a—望江山层状岩体(La/Sm)N—(Tb/Yb)N图解;
b—单斜辉石IVAl—VIAl关系图[41];
c—全岩微量元素Nb/Zr—Th/Zr相对图解Figure 9. Discrimination plots of the nature of mantle source of the Wangjiangshan intrusion
表 1 望江山层状岩体各类岩石主量元素组成(%)
Table 1. Major element concentrations of rocks from the Wangjiangshan intrusion (%)
样号 岩性 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 FeO(T) MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 LOI TOTAL WJS-1 辉长岩 42.44 4.07 14.64 18.92 0.17 5.76 11.11 2.12 0.24 0.13 0.15 99.75 WJS-2 42.11 4.25 14.49 18.78 0.17 5.65 10.87 2.15 0.24 0.14 0.29 99.14 WJS-4 41.54 3.95 14.33 19.53 0.17 5.8 11.1 2.09 0.2 0.13 0.28 99.12 WJS-6 43.43 3.26 15.54 18.12 0.15 5.57 10.69 2.35 0.27 0.16 0.08 99.62 WJS-12 51.15 1.14 15.93 9.98 0.16 6.07 9.06 3.08 1.08 0.14 0.49 98.28 WJS-23 44.56 3.39 17.47 12.94 0.16 4.73 10.65 2.91 0.25 1.67 0.07 98.8 WJS-30 50.17 0.9 18.74 7.83 0.14 6.19 11.4 2.86 0.17 0.5 0.23 99.13 WJS-25 42.53 3.73 15.47 18.22 0.16 5.53 10.89 2.23 0.23 0.13 0.33 99.45 WJS-5 辉长苏长岩 42.16 4.18 14.77 19.07 0.17 5.58 10.82 2.17 0.23 0.13 0.14 99.42 WJS-7 41.98 4.26 14.4 19.22 0.17 5.71 10.91 2.13 0.24 0.11 0 99.13 WJS-8 42.12 3.93 14.62 18.91 0.17 5.85 11.13 2.22 0.21 0.13 0.17 99.46 WJS-9 41.46 4.32 14.23 19.92 0.17 5.79 11.08 2.13 0.2 0.13 0.19 99.62 WJS-13 51.28 1.15 16.01 10.03 0.16 6.06 8.95 3.12 1.1 0.16 0.53 98.55 WJS-14 50.44 1.11 16.5 8.6 0.14 5.99 9.89 3.08 0.94 0.17 1.77 98.63 WJS-15 50.7 1.19 15.5 9.01 0.15 6.49 10.19 2.9 1.03 0.18 1.25 98.59 WJS-22 46.92 1.76 16.3 12.59 0.18 7.34 9.27 3.02 0.47 0.24 0.37 98.46 WJS-24 43.11 3.26 16.49 16.47 0.15 5.12 10.58 2.58 0.25 0.17 0 98.18 WJS-3 43.12 3.49 15.87 17.71 0.16 5.63 10.46 2.38 0.23 0.18 0 99.23 WJS-26 43.28 3.44 16.46 17.05 0.16 5.26 10.54 2.52 0.22 0.17 0.27 99.37 WJS-27 42.85 3.72 15.64 16.7 0.16 5.61 10.71 2.44 0.21 0.21 0.04 98.29 WJS-28 50.65 0.98 17.94 8.37 0.16 6.99 11 2.76 0.15 0.18 0.25 99.43 WJS-29 50.1 0.86 17.77 8.49 0.16 7.09 10.82 2.75 0.15 0.12 0.4 98.71 WJS-31 49.5 0.8 17.6 8.34 0.16 7.33 11.21 2.6 0.12 0.21 0.31 98.18 WJS-32 49.44 0.91 18.04 7.79 0.16 6.72 11.73 2.7 0.15 0.34 0.49 98.47 WJS-34 49.99 0.78 18.99 7.12 0.15 6.01 11.89 2.83 0.16 0.33 0.37 98.62 WJS-35 49.97 0.84 18.88 7.29 0.15 6.18 11.81 2.73 0.15 0.33 0.75 99.08 WJS-36 48.56 2.02 17.77 10.35 0.17 5.76 10.17 2.91 0.28 0.35 0.41 98.75 WJS-20 橄榄辉长苏长岩 47.46 1.65 15.86 12.91 0.19 8.81 8.57 2.85 0.53 0.21 0.34 99.38 WJS-21 46.6 1.66 16.47 12.24 0.18 7.6 9.12 2.94 0.47 0.23 0.62 98.13 表 2 望江山层状岩体各类岩石微量元素与稀土元素组成(×10-6)
Table 2. Trace element and REE concentrations of rocks from the Wangjiangshan intrusion (×10-6)
样号 岩性 V Cr Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Ba La Ce Pr WJS-1 辉长岩 868 0.6 62.56 112 133 109 20.59 3.5 360 17.93 53.17 2.58 0.09 110 4.55 10.97 1.62 WJS-2 901 0.74 63.97 158 123 114 21.33 4.22 362 17.35 59.78 2.92 0.12 112 4.55 10.72 1.63 WJS-4 941 0.77 67.78 1.73 146 114 21.47 2.59 345 15.5 47.79 2.14 0.09 101 3.59 8.96 1.3 WJS-6 896 0.84 80.48 14.11 50.88 93.87 21.31 4.71 433 16.46 56.5 2.15 0.1 123.8 4.58 11.53 1.71 WJS-12 212 67.93 38.95 24.93 19.4 76.27 17.75 24.02 287 28.03 153.45 4.82 0.48 373 13.17 30.6 3.74 WJS-23 272 1.45 31.87 1.6 23.5 84.19 19.26 2.55 679 31.86 58.9 4.61 0.1 142.1 11.46 30.41 4.47 WJS-30 105 247.82 21.62 54.76 6.91 56.82 17.24 1.57 693 15.7 32.23 1.65 0.12 103 4.97 13.23 1.93 WJS-25 901 0.99 70.63 1.28 131 108 20.89 3.23 380 14.92 50.86 2.11 0.13 114.05 3.9 9.33 1.48 WJS-5 辉长苏长岩 936 0.61 63.28 112 137 117 23.15 4.03 375 17.81 59.63 2.96 0.16 114 4.14 10.94 1.57 WJS-7 923 0.65 64.14 38.08 131 117 21.35 3.78 358 16.9 61.17 2.93 0.1 112.25 4.24 10.51 1.57 WJS-8 1096 3.56 89.64 1.69 58.2 117 20.29 2.35 377 16.09 48.04 2.23 0.21 103 3.88 9.77 1.45 WJS-9 974 0.24 67.76 110 147 120 21.07 2.65 355 16.39 49.66 2.4 0.16 104 4.1 10.14 1.51 WJS-13 217 62.69 37.5 26.21 16.67 74.72 18.02 23.11 279 26.81 159.41 4.82 0.45 371 12.86 28.23 3.49 WJS-14 173 162.2 32.67 31.5 38.79 65.88 17.3 18.03 284 25.54 130 4.47 0.42 322 10.57 24 3.26 WJS-15 181 273.31 36.86 60.82 98.24 70.92 17.01 21.07 258 28.65 143.75 5.04 0.44 342 11.12 26.25 3.63 WJS-22 240 176 48.02 105 61.44 97.79 18.68 6.36 279 31.4 149 4.18 0.37 281 8.48 21.72 3.29 WJS-24 524 1.04 64.71 5.83 43.35 93.81 20.44 3.92 474 15.14 49.99 2.13 0.16 130 4.64 11.45 1.58 WJS-3 605 1.71 68.27 1.33 43.9 106 22.94 3.92 458 15.9 58.35 2.54 0.1 131 4.97 12.05 1.72 WJS-26 534 0.77 63.74 6.79 42.94 95 21.96 2.88 481 15.29 50.86 2.51 0.09 128 4.19 10.7 1.59 WJS-27 540 0.8 64.42 6.56 43.63 102 21.53 3.02 439 16.66 55.12 2.73 0.13 125 4.49 11.15 1.61 WJS-28 98.62 215 22.55 42.2 6.99 57.59 16.16 1.12 637 13.57 31.86 1.54 0.03 106 3.47 8.88 1.3 WJS-29 106 241 24.15 48.12 7.35 60.55 16.37 1.15 637 13.32 28.83 1.14 0.06 106 3.45 8.72 1.22 WJS-31 109 291 24.77 60.21 6.54 63.77 16.37 0.78 674 10.59 20.17 0.69 0.01 83 2.75 6.48 1.1 WJS-32 97.64 282 21.45 58.78 6.61 58.07 15.58 1.08 650 10.65 22.12 0.89 0.07 80 3.05 7.52 1.07 WJS-34 21.4 23.63 2.19 5.91 2.2 22.02 5.31 94.71 41 20 245.75 6.45 0 325 63.01 127.42 14.24 WJS-35 96.14 275 20.48 58.21 5.81 54.42 17.5 1.32 688 10.44 20.72 0.8 0.01 84 3.06 7.5 1.19 WJS-36 167 61.45 25.79 22.66 13.09 68.75 20.35 4.15 646 21.92 69.35 3.69 0.25 161 6.99 17.52 2.39 WJS-20 橄榄辉长苏长岩 212 176 56.29 195 95.34 93.82 17.74 7.47 258 28.61 155 4.26 0.3 293 7.5 19.63 2.79 WJS-21 219 165 49.45 128 60.85 89.18 18.16 6.83 278 28.71 141 4.09 0.22 285 7.63 20.57 2.99 样号 岩性 Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Hf Ta Pb Th U Cs WJS-1 辉长岩 8.3 2.58 1.56 3.11 0.52 3.16 0.66 1.91 0.25 1.63 0.2 1.6 0.37 1.66 0.38 0.08 0.12 WJS-2 8.71 2.7 1.31 2.96 0.56 3.15 0.61 1.88 0.24 1.52 0.21 2.11 0.34 1.73 0.44 0.11 0.15 WJS-4 7.42 2.21 1.17 2.68 0.48 2.8 0.47 1.36 0.21 1.16 0.21 1.32 0.22 1.55 0.22 0.07 0.11 WJS-6 9.08 2.54 1.39 2.85 0.48 3.34 0.62 1.98 0.26 1.49 0.23 1.79 0.2 1.75 0.36 0.12 0.14 WJS-12 17.09 4.45 1.38 5.04 0.77 5.38 1.19 3.36 0.47 2.69 0.48 4.49 0.39 6.63 1.86 0.54 0.76 WJS-23 22.18 6.15 2.45 6.98 0.99 6.08 1.2 3.12 0.43 2.15 0.34 1.92 0.35 2.13 0.42 0.13 0.07 WJS-30 9.81 2.8 1.31 3.12 0.5 2.92 0.56 1.66 0.2 1.29 0.24 0.99 0.13 1.58 0.19 0.05 0.07 WJS-25 7.42 2.29 1.26 2.37 0.44 2.99 0.53 1.54 0.22 1.35 0.2 1.52 0.25 1.84 0.29 0.09 0.11 WJS-5 辉长苏长岩 7.78 2.74 1.26 3.01 0.53 3.03 0.64 1.85 0.29 1.25 0.19 1.74 0.24 1.81 0.37 0.1 0.15 WJS-7 8.25 2.3 1.43 3.39 0.49 3.06 0.68 1.96 0.28 1.91 0.22 1.86 0.3 1.79 0.33 0.09 0.12 WJS-8 7.95 2.6 1.47 3 0.54 3.23 0.76 1.61 0.26 1.64 0.19 1.55 0.26 1.61 0.27 0.06 0.1 WJS-9 7.9 2.42 1.35 3.16 0.51 3.32 0.65 1.79 0.25 1.52 0.27 1.59 0.26 1.69 0.26 0.07 0.14 WJS-13 15.23 3.67 1.28 4.36 0.81 4.53 1.08 2.86 0.45 2.76 0.41 4.4 0.34 6.55 1.93 0.55 0.74 WJS-14 14.88 3.69 1.39 4.59 0.7 4.28 0.95 2.62 0.41 2.35 0.36 3.75 0.29 5.81 1.38 0.43 0.78 WJS-15 16.72 3.69 1.56 4.76 0.76 5.45 1.02 3.19 0.43 2.8 0.48 3.77 0.36 6.19 1.4 0.45 0.79 WJS-22 16.61 4.16 1.68 5.45 0.82 5.76 1.22 3.32 0.5 3.05 0.41 3.95 0.32 3.22 0.6 0.19 0.23 WJS-24 7.94 2.53 1.53 2.86 0.44 2.88 0.6 1.81 0.21 1.13 0.19 1.64 0.21 1.86 0.3 0.09 0.13 WJS-3 9.09 2.6 1.46 3.09 0.52 3.15 0.58 1.75 0.22 1.62 0.22 1.56 0.19 1.89 0.32 0.1 0.11 WJS-26 7.71 2 1.44 2.8 0.51 2.73 0.55 1.58 0.21 1.2 0.19 1.59 0.25 1.79 0.25 0.07 0.14 WJS-27 8.17 2.58 1.36 3.06 0.51 3.27 0.59 1.61 0.22 1.48 0.2 1.44 0.23 1.72 0.24 0.07 0.17 WJS-28 6.71 1.88 1.15 2.71 0.38 2.23 0.48 1.54 0.16 1.19 0.17 0.88 0.12 1.5 0.11 0.03 0.06 WJS-29 6.27 1.84 1.07 2.28 0.42 2.24 0.5 1.44 0.19 1.09 0.21 0.75 0.09 1.73 0.11 0.03 0.05 WJS-31 5.54 1.63 0.94 1.88 0.33 2.28 0.49 1.35 0.14 0.87 0.15 0.71 0.09 1.19 0.08 0.03 0.03 WJS-32 6.11 1.66 1.11 2.02 0.37 2.09 0.37 1.18 0.15 1.04 0.16 0.77 0.09 1.1 0.12 0.04 0.08 WJS-34 54.01 9.31 1.4 7.71 0.96 4.49 0.67 1.99 0.26 1.71 0.25 7.84 0.56 38.56 11.78 3.38 1.47 WJS-35 6.07 1.66 0.99 2.08 0.35 2.12 0.36 1.14 0.16 0.77 0.14 0.8 0.07 1.08 0.11 0.03 0.09 WJS-36 12.26 3.57 1.67 4.3 0.66 3.76 0.79 2.39 0.31 2.09 0.27 1.87 0.34 2.49 0.4 0.11 0.16 WJS-20 橄榄辉长苏长岩 13.79 3.53 1.57 4.62 0.81 5.09 1 2.84 0.46 2.59 0.42 3.99 0.26 3.54 0.62 0.2 0.29 WJS-21 15.57 4.11 1.54 4.74 0.77 5.13 1.05 3.02 0.45 2.59 0.4 3.53 0.22 3.15 0.5 0.18 0.24 表 3 望江山岩体不同岩相铂族元素组成(×10-9)
Table 3. Platinum group element concentrations of samples from the Wangjiangshan intrusion (×10-9)
样号 岩性 Ir Ru Rh Pt Pd ΣPGE WJS-4 辉长岩 0.003 0.184 0.124 5.083 5.775 11.169 WJS-6 辉长岩 0.002 0.176 0.028 0.028 0.082 0.316 WJS-25 辉长岩 0.025 0.212 0.391 4.041 10.612 15.281 WJS-14 辉长苏长岩 0.052 0.215 0.123 6.586 6.845 13.821 WJS-24 辉长苏长岩 0.007 0.165 0.099 0.358 2.097 2.726 WJS-28 辉长苏长岩 0.008 0.141 0.087 0.183 0.274 0.693 WJS-29 辉长苏长岩 0.010 0.134 0.136 1.096 4.207 5.583 WJS-26 辉长苏长岩 0.002 0.183 0.027 0.066 0.104 0.382 WJS-31 辉长苏长岩 0.008 0.180 0.125 0.346 1.389 2.048 WJS-20 橄榄辉长苏长岩 0.111 0.260 0.375 2.389 8.271 11.406 WJS-21 橄榄辉长苏长岩 0.037 0.277 0.200 0.624 0.713 1.851 表 4 望江山岩体橄榄辉长苏长岩中橄榄石成分(%)
Table 4. Major element concentrations of olivine from the Wangjiangshan intrusion (%)
样号 WJS21-1 WJS21-3 WJS21-2 WJS21-4 WJS20-2 WJS20-3 Na2O 0.00 0.01 0.04 0.00 0.06 0.03 K2O 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 FeO 40.07 38.91 38.69 36.64 41.17 38.89 MgO 24.54 25.21 24.70 26.69 24.74 26.15 P2O5 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.04 0.01 MnO 0.71 0.61 0.74 0.69 0.57 0.54 Al2O3 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 CaO 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Cr2O3 0.02 0.02 0.00 0.02 0.04 0.00 SiO2 35.17 35.27 34.93 35.78 34.03 34.39 TiO2 0.00 0.06 0.00 0.06 0.00 0.01 NiO 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.12 0.02 0.06 Total 100.55 100.18 99.20 99.98 100.66 100.07 Fo值 52.20 53.60 53.20 56.50 51.70 54.50 表 5 望江山岩体单斜辉石主量元素分析结果(%)
Table 5. Major elements of clinopyroxene from the Wangjiangshan intrusion (%)
点号 岩性 Na2O K2O FeO MgO P2O5 MnO Al2O3 CaO Cr2O3 SiO2 TiO2 NiO Total Wo En Fs WJS6-1 辉长岩 0.31 0.00 8.84 14.04 0.00 0.34 1.95 21.91 0.01 52.12 0.47 0.00 99.98 46.10 41.00 12.90 WJS6-2 0.31 0.00 10.54 14.78 0.00 0.29 2.34 19.42 0.36 51.24 0.64 0.00 99.93 41.40 43.80 14.80 WJS6-3 0.35 0.00 10.45 14.20 0.00 0.28 2.56 19.93 0.01 50.95 0.87 0.00 99.60 42.70 42.30 15.00 WJS6-4 0.42 0.00 8.61 14.49 0.00 0.26 1.16 21.91 0.04 52.64 0.05 0.06 99.64 46.30 42.60 11.20 WJS25-1 0.42 0.01 9.53 14.58 0.01 0.26 2.18 21.33 0.05 50.45 0.60 0.05 99.46 46.70 44.40 9.00 WJS24-1 辉长苏长岩 0.24 0.01 8.55 14.54 0.00 0.24 2.17 21.30 0.03 51.22 0.56 0.00 98.86 45.20 42.90 11.90 WJS24-2 0.21 0.00 8.83 14.79 0.00 0.33 1.00 21.82 0.00 52.39 0.30 0.01 99.67 45.40 42.80 11.80 WJS24-3 0.26 0.00 7.84 15.62 0.00 0.20 2.07 20.57 0.02 52.10 0.47 0.00 99.15 43.00 45.40 11.60 WJS24-4 0.29 0.01 10.30 14.65 0.00 0.23 2.08 20.13 0.01 51.56 0.53 0.00 99.79 42.60 43.10 14.30 WJS26-1 0.23 0.00 8.86 14.32 0.00 0.34 2.16 20.46 0.01 52.36 0.74 0.07 99.53 43.30 42.10 14.60 WJS26-2 0.24 0.01 8.64 14.43 0.00 0.23 2.33 21.95 0.05 51.24 0.54 0.09 99.74 46.60 42.60 10.70 WJS26-3 0.33 0.01 8.48 14.08 0.00 0.26 2.29 21.46 0.03 51.18 0.64 0.01 98.77 45.90 41.90 12.20 WJS26-4 0.30 0.01 8.56 14.62 0.00 0.29 2.20 20.33 0.01 51.74 0.57 0.00 98.62 42.90 43.00 14.10 WJS31-1 0.44 0.00 8.00 14.63 0.00 0.31 2.38 22.22 0.04 52.19 0.72 0.03 100.96 46.90 43.00 10.10 WJS31-2 0.26 0.01 8.86 14.93 0.00 0.28 2.02 19.47 0.06 52.52 0.35 0.06 98.82 41.30 44.00 14.70 WJS31-3 0.38 0.00 7.65 14.57 0.00 0.40 2.00 22.13 0.07 51.70 0.39 0.01 99.31 47.30 43.30 9.50 WJS31-4 0.28 0.00 8.14 14.86 0.00 0.31 2.11 21.24 0.04 51.44 0.63 0.06 99.10 45.00 43.80 11.20 WJS34-1 0.36 0.01 7.47 14.51 0.00 0.18 1.70 22.13 0.06 52.28 0.31 0.00 99.00 46.50 42.40 11.00 WJS34-2 0.40 0.00 8.57 14.63 0.00 0.34 2.11 21.77 0.09 51.89 0.65 0.00 100.45 46.10 43.10 10.70 WJS34-3 0.32 0.00 8.23 14.54 0.00 0.32 2.00 22.06 0.12 51.70 0.42 0.00 99.71 46.80 42.90 10.30 WJS34-4 0.17 0.00 6.89 14.89 0.00 0.34 0.53 23.63 0.11 52.66 0.15 0.00 99.37 48.90 42.80 8.30 表 6 望江山岩体斜方辉石主量元素含量(%)
Table 6. Major element concentrations of orthopyroxene from the Wangjiangshan intrusion (%)
点号 岩性 Na2O K2O FeO(T) MgO P2O5 MnO Al2O3 CaO Cr2O3 SiO2 TiO2 NiO Total Wo En Fs WJS6-1 辉长岩 0.04 0.01 22.33 22.40 0 0.63 0.64 1.15 0.05 53.14 0.17 0 100.55 2.3 63.5 34.1 WJS6-2 0 0 23.84 21.77 0 0.56 0.71 0.9 0 52.64 0.29 0.04 100.74 1.9 62 36.2 WJS21-1 橄榄辉长苏长岩 0.03 0 22 22.17 0 0.52 0.63 1.24 0.03 53.03 0.24 0.02 99.91 2.5 62.8 34.7 WJS21-2 0 0.02 21.19 22.53 0 0.64 0.77 0.82 0.01 53.43 0.2 0 99.6 1.7 64.4 34 WJS21-3 0 0.01 22.36 22.33 0 0.47 0.65 0.66 0.04 53.4 0.01 0 99.92 1.3 63.2 35.5 WJS24-1 辉长苏长岩 0.01 0.01 18.97 25.23 0 0.55 0.85 0.48 0.01 54.34 0.29 0 100.73 1 69.7 29.4 WJS24-2 0 0.01 20.4 23.68 0 0.48 0.77 0.47 0.03 53.51 0.06 0 99.42 1 66.8 32.3 WJS24-3 0.01 0 19.07 24.38 0 0.59 1 0.73 0 53.73 0.2 0.01 99.72 1.5 68.5 30.1 WJS26-1 0.01 0.02 19.09 24.05 0 0.5 0.88 0.95 0.05 53.92 0.34 0.12 99.93 1.9 67.9 30.2 WJS26-2 0.07 0 19.9 23.5 0 0.6 1.12 0.77 0.01 53.45 0.23 0 99.65 1.6 66.7 31.7 WJS31-1 0.02 0 17.21 24.58 0 0.49 1.29 2.66 0.03 53.75 0.17 0 100.2 5.3 68.6 26 WJS31-2 0.04 0 18.6 25.08 0 0.65 0.76 0.6 0 54.09 0.16 0 99.97 1.2 69.8 29 WJS31-3 0 0 18.24 25.04 0 0.53 0.9 1.42 0.02 54.02 0.22 0 100.39 2.8 69.5 27.7 WJS31-4 0.15 0.04 17.28 21.56 0 0.48 1.42 3.01 0.89 53.4 0.3 0 98.53 6.5 64.5 29 WJS31-5 0.01 0 18.27 25.1 0 0.77 0.88 0.69 0.06 53.95 0.14 0 99.87 1.4 70.1 28.5 WJS34-1 0.03 0 17.74 24.34 0 0.66 0.71 3.33 0.04 53.51 0.09 0 100.45 6.7 68.6 24.6 WJS34-2 0 0.01 18.7 24.94 0 0.61 0.87 0.66 0.04 53.67 0.21 0 99.71 1.3 69.8 28.9 表 7 望江山岩体辉长岩和辉长苏长岩中磁铁矿—钛铁矿成分(%)
Table 7. Magnetite-ilmenite concentrations of rocks from gabbro and gabbronorite of the Wangjiangshan intrusion (%)
WJS-25-1 WJS-25-3 WJS-26-4 WJS-26-1 WJS-26-2 WJS-26-3 WJS-30 WJS-34 辉长岩 辉长苏长岩 钛铁矿 磁铁矿 钛铁矿 磁铁矿 钛铁矿 磁铁矿 磁铁矿 钛铁矿 钛铁矿 磁铁矿 磁铁矿 磁铁矿 SiO2 0.09 0.05 0.038 0.03 0 0.07 0.06 0 0 0.07 0.04 0.06 TiO2 51.36 0.2 52.83 0.4 52.1 0.34 0.18 53.01 46.96 0.34 0.12 0.13 Al2O3 0.05 0.37 0 0.46 0 0.03 0.48 0 0.04 0.03 0.4 0.26 P2O5 0.05 0.09 0.02 0 0.05 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 FeO(T) 46.06 91.06 44.1 90.3 47.69 90.72 91.75 45.62 52.92 90.72 91.52 93.65 MnO 1 0.03 0.97 0 0.94 0 0.05 1.42 0.64 0 0.01 0.03 MgO 1.24 0.07 1.85 0.07 0.26 0 0.13 1.19 0.9 0 0.21 0.17 CaO 0 0.02 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Na2O 0.11 0.1 0.02 0.18 0 0.05 0.03 0 0 0.05 0.03 0 K2O 0.01 0.01 0 0.01 0.01 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Cr2O3 0.14 0.01 0.03 0.08 0.04 0.09 0.09 0.08 0 0.09 1.3 1.81 NiO 0.02 0 0 0.03 0 0.05 0.1 0 0 0.05 0 0.06 Total 100.12 92.02 99.87 91.58 101.09 91.35 92.87 101.39 101.53 91.35 93.62 96.17 -
[1] Barnes S J. The effect of trapped liquid crystallization on cumulus mineral compositions in layered intrusions[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1986, 93(4):524~531. doi: 10.1007/BF00371722 [2] Tegner C, Thy P, Holness M B, et al. Differentiation and compaction in the Skaergaard intrusion[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2009, 50(5):813~840. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp020 [3] Veksler I V. Extreme iron enrichment and liquid immiscibility in mafic intrusions:Experimental evidence revisited[J]. Lithos, 2009, 111(1/2):72~82. [4] Niu M L, Zhu G, Liu G S, et al. Tectonic setting and deep processes of Mesozoic magmatism in Middle-South segment of the Tan-Lu fault[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 2002, 37(4):393~404. [5] Li C S, Xu Z H, De Waal S A, et al. Compositional variations of olivine from the Jinchuan Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, western China:implications for ore genesis[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2004, 39(2):159~172. doi: 10.1007/s00126-003-0389-5 [6] 钟宏, 胡瑞忠, 朱维光, 等.层状岩体的成因及成矿作用[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(2):159~172. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.02.013ZHONG Hong, HU Ruizhong, ZHU Weiguang, et al. Genesis and mineralization of layered intrusions[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(2):159~172. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.02.013 [7] Naldrett A J, Lightfoot P C, Fedorenko V, et al. Geology and geochemistry of intrusions and flood basalts of the Noril'sk region, USSR, with implications for the origin of the Ni-Cu ores[J]. Economic Geology, 1992, 87(4):975~1004. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.87.4.975 [8] Naldrett A J, Fedorenko V A, Asif M, et al. Controls on the composition of Ni-Cu sulfide deposits as illustrated by those at Noril'sk, Siberia[J]. Economic Geology, 1996, 91(4):751~773. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.91.4.751 [9] Song X Y, Zhou M F, Hou Z Q, et al. Geochemical constraints on the mantle source of the upper Permian Emeishan continental flood basalts, Southwestern China[J]. International Geology Review, 2001, 43(3):213~225. doi: 10.1080/00206810109465009 [10] Xiao L, Xu Y G, Mei H J, et al. Distinct mantle sources of low-Ti and high-Ti basalts from the western Emeishan large igneous province, SW China:implications for plume-lithosphere interaction[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 228(3/4):525~546. doi: 10.1016-j.epsl.2004.10.002/ [11] Song X Y, Li X R. Geochemistry of the Kalatongke Ni-Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposit, NW China:implications for the formation of magmatic sulfide mineralization in a postcollisional environment[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2009, 44(3):303~327. doi: 10.1007/s00126-008-0219-x [12] Wei B, Wang C Y, Li C S, et al. Origin of PGE-depleted Ni-Cu sulfide mineralization in the Triassic Hongqiling No.7 orthopyroxenite intrusion, Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Northeastern China[J]. Economic Geology, 2013, 108(8): 1813~1831. [13] Piña R, Gervilla F, Ortega L, et al. Geochemical constraints on the origin of the Ni-Cu sulfide ores in the Tejadillas prospect (Cortegana Igneous Complex, SW Spain)[J]. Resource Geology, 2012, 62(3):263~280. [14] Li C S, Zhang Z W, Li W Y, et al. Geochronology, petrology and Hf-S isotope geochemistry of the newly-discovered Xiarihamu magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide deposit in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Lithos, 2015, 216~217:224~240. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.01.003 [15] Wang M X, Wang C Y, Sun Y L. Mantle source, magma differentiation and sulfide saturation of the~637 Ma Zhouan mafic-ultramafic intrusion in the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, Central China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 228:206~222. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.01.015 [16] Zhou J C, Wang X L, Qiu J S, et al. Geochemistry of Meso-and Neoproterozoic mafic-ultramafic rocks from northern Guangxi, China:Arc or plume magmatism?[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2003, 19(1):9~18. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200805003 [17] Zhou M F, Yan D P, Kennedy A K, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronological and geochemical evidence for Neoproterozoic arc-magmatism along the western margin of the Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 196(1/2):51~67. [18] Zhao J H, Zhou M F. Melting of newly formed mafic crust for the formation of neoproterozoic I-type granite in the Hannan Region, South China[J]. Journal of Geology, 2009, 117(1):54~70. doi: 10.1086/593321 [19] Wang M X, Nebel O, Wang C Y. The flaw in the crustal 'Zircon Archive':mixed Hf isotope signatures record progressive contamination of late-stage liquid in mafic-ultramafic layered intrusions[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2016, 57(1):27~52. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egv072 [20] Dong Y P, Liu X M, Santosh M, et al. Neoproterozoic subduction tectonics of the northwestern Yangtze Block in South China:Constrains from zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of mafic intrusions in the Hannan Massif[J]. Precambrian Research, 2011, 189(1/2):66~90. [21] Ling W L, Gao S, Zhang B R, et al. Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the northwestern Yangtze craton, South China:implications for amalgamation and break-up of the Rodinia Supercontinent[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 122(1/4):111~140. doi: 10.1016-S0301-9268(02)00222-X/ [22] Li X H, Li Z X, Sinclair J A, et al. Reply to the comment by Zhou et al. on: "Revisiting the "Yanbian Terrane": Implications for Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the western Yangtze Block, South China"[Precambrian Res. 151(2006) 14~30] [Precambrian Res. 154(2007) 153~157] [J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 155(3/4): 318~323. [23] Zheng Y F, Zhang S B, Zhao Z F, et al. Contrasting zircon Hf and O isotopes in the two episodes of Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China:Implications for growth and reworking of continental crust[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96(1/2):127~150. [24] Chen J F, Foland K A, Xing F M, et al. Magmatism along the southeast margin of the Yangtze block:Precambrian collision of the Yangtze and Cathysia blocks of China[J]. Geology, 1991, 19(8):815~818. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<0815:MATSMO>2.3.CO;2 [25] Zhao J H, Zhou M F, Yan D P, et al. Reappraisal of the ages of Neoproterozoic strata in South China:No connection with the Grenvillian orogeny[J]. Geology, 2011, 39(4):299~302. doi: 10.1130/G31701.1 [26] Zhao J H, Zhou M F. Neoproterozoic adakitic plutons in the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, China:Partial melting of a thickened lower crust and implications for secular crustal evolution[J]. Lithos, 2008, 104(1/4):231~248. [27] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 马中平, 等.南秦岭中段西乡群火山岩岩石成因[J].西北地质, 2009, 42(2):1~37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2009.02.001Xia Linqi, Xia Zuchun, Ma Zhongping, et al. Petrogenesis of volcanic rocks from Xixiang Group in middle part of South Qinling Mountains[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2009, 42(2):1~37. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2009.02.001 [28] 李行, 白文吉, 陈方伦, 等.扬子地块北缘和西缘前寒武纪镁铁层状杂岩及含铂性[M].西安:西北大学出版社, 1995, 18~31.LI Xing, BAI Wenji, CHEN Fanglun, et al. Precambrian mafic layered complexes and platinum-bearing properties in the northern and Western margins of the Yangtze massif[M]. Xi'an:Northwest University Press, 1995, 18~31. (in Chinese) [29] 苏犁.中国中西部几个新元古代镁铁、超镁铁岩体研究及对Rodinia超大陆裂解事件的制约[D].西安: 西北大学, 2004.SU Li. Studies of Neoproterozoic mafic and ultramafic intrusions in western-central China and their constraints on breakup of Rodinia supercontinent[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2004. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 郑茂荣, 卢一伦, 杨尊西, 等. 1: 20万汉中幅区域地质图[Z].陕西省地质局地质测量大队, 1959.ZHENG Maorong, LU Yilun, YANG Zunxi, et al. 1: 200, 000 Hanzhong regional geological map[Z]. Geological Survey Brigade of Shaanxi Provincial Geological Bureau, 1959. [31] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313~345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 [32] Morimoto N. Nomenclature of pyroxenes[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2007, 39(1):55~76. [33] Carmichael I S E. The iron-titanium oxides of salic volcanic rocks and their associated ferromagnesian silicates[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1966, 14(1):36~64. doi: 10.1007/BF00370985 [34] Anderson A T. Oxidation of the LaBlache Lake Titaniferous magnetite deposit, Quebec[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1968, 76(5):528~547. doi: 10.1086/627358 [35] Spencer K J, Lindsley D H. A solution model for coexisting iron titanium oxides[J]. American Mineralogist, 1981, 66(11~12):1189~1201. [36] Stormer J C Jr. The effects of recalculation on estimates of temperature and oxygen fugacity from analyses of multicomponent iron-titanium oxides[J]. American Mineralogist, 1983, 68(5):586~594. [37] Lepage L D. ILMAT:an excel worksheet for ilmenite-magnetite geothermometry and geobarometry[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2003, 29(5):673~678. [38] Staudigel H, Hart S R. Alteration of basaltic glass:Mechanisms and significance for the oceanic crust-seawater budget[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1983, 47(3):337~350. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(83)90257-0 [39] Pearce J A, Van Der Laan S R, Arculus R J, et al. Boninite and harzburgite from Leg 125(Bonin-Mariana forearc): A case study of magma genesis during the initial stages of subduction[A]. Fryer P, Pearce J A, Stolling L B, et al. Proceeding of the Ocean Drilling Program[C]. ODP Sci Res, 1992, 623~659. [40] Barnes S J, Naldrett A J, Gorton M P. The origin of the fractionation of platinum-group elements in terrestrial magmas[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, 53(3~4):303~323. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(85)90076-2 [41] Seyler M, Bonatti E. Na, Al IV and Al VI in clinopyroxenes of subcontinental and suboceanic ridge peridotites:a clue to different melting processes in the mantle?[J]. Earth and Planet Science Letters, 1994, 122(3~4):281~289. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90002-7 [42] 陈列锰, 宋谢炎, 聂晓勇, 等.甘肃金川Ⅱ号岩体辉石化学特征及其地质意义[J].矿物岩石, 2008, 28(1):88~96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2008.01.013CHEN Liemeng, SONG Xieyan, NIE Xiaoyong, et al. Mineral chemistry and geological significance of pyroxene from segment Ⅱ of the Jinchuan intrusion, Gansu province[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2008, 28(1):88~96. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2008.01.013 [43] Eugster H P, Wones D R. Stability Relations of the Ferruginous Biotite, Annite[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1962, 3(1):82~125. doi: 10.1093/petrology/3.1.82 [44] Brey G P, Köhler T. Geothermobarometry in Four-phase Lherzolites Ⅱ. new thermobarometers, and practical assessment of existing thermobarometers[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1990, 31(6): 1353~1378. [45] Nimis P, Ulmer P. Clinopyroxene geobarometry of magmatic rocks Part 1:An expanded structural geobarometer for anhydrous and hydrous, basic and ultrabasic systems[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1998, 133(1/2):122~135. [46] Nimis P. A clinopyroxene geobarometer for basaltic systems based on crystal-structure modeling[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1995, 121(2):115~125. doi: 10.1007/s004100050093 [47] Li C, Naldrett A J. Geology and petrology of the Voisey's Bay intrusion:reaction of olivine with sulfide and silicate liquids[J]. Lithos, 1999, 47(1/2):1~31. doi: 10.1016-S0024-4937(99)00005-5/ [48] Li Q W, Zhao J H. Nature and thermal state of the lithosphere beneath the western margin of the Yangtze Block in South China during the neoproterozoic[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2018, 126(3):343~360. doi: 10.1086/697306 [49] Wang X C, Li X H, Li W X, et al. The Bikou basalts in the northwestern Yangtze block, South China:Remnants of 820~810 Ma continental flood basalts?[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2008, 120(11~12):1478~1492. doi: 10.1130/B26310.1 [50] Barnes S J, Maier W D. The fractionation of Ni, Cu, and the noble metals in silicate and sulphide liquids[A]. Keays R R, Lesher C M, Lightfoot P C, et al. Dynamic Processes in Magmatic ore deposits and their Application in Mineral Exploration, 1999, Short Course Volume 13[M]. Geologic Association of Canada, 69~106. [51] 郑光高, 崔建军, 刘晓春, 等.汉南杂岩余家山铜镍矿成矿时代与岩浆源区性质研究——来自锆石U-Pb测年和Lu-Hf同位素的制约[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(5):661~672. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.05.004ZHENG Guanggao, CUI Jianjun, LIU Xiaochun, et al. Metallogenic ages and the nature of magma source of the Yujiashan Cu-Ni deposit, Hannan complex:constraints from zircon u-pb dating and Lu-Hf isotope[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(5):661~672. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.05.004 [52] Irvine T N. Crystallization sequences in the Muskox intrusion and other layered intrusions-Ⅱ. Origin of chromitite layers and similar deposits of other magmatic ores[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1975, 39(6~7): 991~1020. [53] Keays R R, Lightfoot P C. Crustal sulfur is required to form magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide deposits:evidence from chalcophile element signatures of Siberian and Deccan Trap basalts[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2010, 45(3):241~257. doi: 10.1007/s00126-009-0271-1 [54] Naldrett A J. From the mantle to the bank:The life of a Ni-Cu-(PGE) sulfide deposit[J]. South African Journal of Geology, 2010, 113(1):1~32. [55] 李献华, 王选策, 李武显, 等.华南新元古代玄武质岩石成因与构造意义:从造山运动到陆内裂谷[J].地球科学, 2008, 37(4):382~398. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.04.007LI Xianhua, WANG Xuance, LI Wuxian, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of Neoproterozoic basaltic rocks in South China:from orogenesis to intracontinental rifting[J]. Geosciences, 2008, 37(4):382~398. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.04.007 [56] Loucks R R. Discrimination of ophiolitic from nonophiolitic ultramafic-mafic allochthons in orogenic belts by the Al/Ti ratio in clinopyroxene[J]. Geology, 1990, 18(4):346~349. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<0346:DOOFNU>2.3.CO;2 [57] Deng Q, Wang J, Wang Z J, et al. Continental flood basalts of the Huashan Group, northern margin of the Yangtze block-implications for the breakup of Rodinia[J]. International Geology Review, 2013, 55(15):1865~1884. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.799257 [58] Zhao J H, Li Q W, Liu H, et al. Neoproterozoic magmatism in the western and northern margins of the Yangtze Block (South China) controlled by slab subduction and subduction-transform-edge-propagator[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 187:1~18. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.10.004 [59] 王平安, 陈毓川.秦岭造山带构造-成矿旋回与演化[J].地质力学学报, 1997, 3(1):10~20. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19970102&journal_id=dzlxxbWANG Ping'an, CHEN Yuchuan. Tectono minerogenic cycles and minerogenetic evolution through geological history in the Qinling orogenic belt[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 1997, 3(1):10~20. (in Chinese with English abstract http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19970102&journal_id=dzlxxb [60] Himmelberg G R, Loney R A. Characteristics and petrogenesis of Alaskan-type ultramafic-mafic intrusions, southeastern Alaska[J]. Geological Society of America, Abstracts with Programs; (United States), 1995, 25:5. [61] Thakurta J, Ripley E M, Li C S. Geochemical constraints on the origin of sulfide mineralization in the Duke Island Complex, southeastern Alaska[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013, 9(7):Q07003. [62] Le Bas M J. The role of aluminum in igneous clinopyroxenes with relation to their parentage[J]. American Journal of Science, 1962, 260(4):267~288. doi: 10.2475/ajs.260.4.267 [63] Pearce J A, Norry M J. Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y, and Nb variations in volcanic rocks[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1979, 69(1):33~47. doi: 10.1007/BF00375192 -





 下载:
下载: