THE INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT NEWMARK DISPLACEMENT MODELS ON SEISMIC LANDSLIDE HAZARD ASSESSMENT: A CASE STUDY OF TIANSHUI AREA, CHINA
-
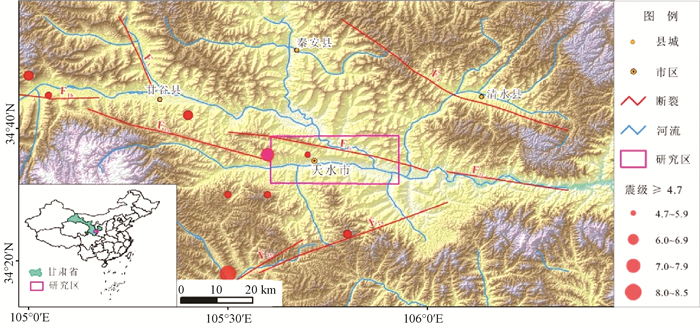
摘要: 近年来,Newmark累积位移分析方法经过不断的改进和应用成为国际主流的地震滑坡危险性评估方法之一,众多学者基于位移预测模型开展区域地震滑坡危险性评估,然而鲜有针对不同位移模型对评估结果影响的定量研究。以天水地区为例,基于不同的位移预测模型开展地震滑坡危险性评估,对比位移模型对地震滑坡危险性评估的影响,探讨建立适用于我国的Newmark位移预测模型。结果表明:基于不同位移预测模型评估所得的地震滑坡危险性结果整体趋势一致,均能区分区域地震滑坡危险性等级的相对差异,但在同样的危险性分级标准下,所得中、高危险区的分布范围有较大差异。这与位移模型的函数形式及其区域相关性有关,在引入Newmark累积位移分析方法开展地震滑坡危险性评估的同时,应尽快建立考虑地震动衰减特征和工程地质背景的Newmark位移预测模型,为中国潜在地震滑坡危险性预测评估、震后滑坡快速评估等提供技术支撑。
-
关键词:
- 地震滑坡 /
- 危险性评估 /
- Newmark位移预测模型 /
- 天水地区
Abstract: Recent years, the Newmark sliding-block model is one of the most wildly-used methods for assessing the stability of slopes during earthquakes; however, the influence of different Newmark displacement models on seismic landslide hazard assessments need to be investigated and quantified. Through the comparison between the displacements estimated by various Newmark displacement models in the Tianshui area, the influence of Newmark displacement models on seismic landslide hazard assessments are discussed. The results show that the overall tendency of the seismic landslide risk assessment based on different displacement prediction models is consistent; however, due to the region dependent and various function forms of these models, there is a great difference in the distribution of moderate and high seismic landslide hazard area. It suggests that a Newmark displacement prediction model considering the attenuation characteristics of ground motion and the engineering geological background of China should be established as soon as possible, which will provide support for the potential seismic landslide hazard assessment and the rapid assessment of post-earthquake landslide. -
表 1 不同位移公式参数特征
Table 1. Parameter characteristics of different displacement formulas
位移公式 震级范围
(记录数)临界加速度
范围(g)相关系数
(标准差)公式(3) 5.8~7.5(11) 0.02~0.40 0.87(0.409) 公式(4) 5.3~7.6(875) 0.05~0.40 0.71(0.656) 公式(5) 6.7~7.4(290) 0.01~0.40 0.89(0.295) 公式(6) 6.7(20) 0.01~0.20 0.90(0.172) 表 2 不同位移预测公式多得位移区间分布
Table 2. Displacement interval distribution based on different displacement prediction formulas
位移公式 Newmark位移(占研究区总面积百分比) 0 cm~0.5 cm 0.5 cm~5.0 cm 5.0 cm~50 cm >50 cm 公式(3) 90.7% 7.4% 1.9% 0.1% 公式(4) 97.1% 2.0% 0.5% 0.4% 公式(5) 95.1% 3.4% 1.4% 0.1% 公式(6) 98.0% 1.3% 0.7% 0 -
[1] 吴树仁, 石菊松, 张春山, 等.地质灾害风险评估技术指南初论[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(8):995~1005. http://www.doc88.com/p-0092023776545.htmlWU Shuren, SHI Jusong, ZHANG Chunshan, et al. Preliminary discussion on technical guideline for geohazard risk assessment[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(8):995~1005. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.doc88.com/p-0092023776545.html [2] 殷跃平.汶川八级地震滑坡高速远程特征分析[J].工程地质学报, 2009, 17(2):153~166. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/90a519528762caaedc33d407.htmlYIN Yueping. Rapid and long run-out features of landslides triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(2):153~166. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/90a519528762caaedc33d407.html [3] 张永双, 石菊松, 孙萍, 等.汶川地震内外动力耦合及灾害实例[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(2):131~141. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090203&flag=1ZHANG Yongshuang, SHI Jusong, SUN Ping, et al. Coupling between endogenic and exogenic geological processes in the Wenchuan earthquake and example analysis of geo-hazards[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(2):131~141. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090203&flag=1 [4] 许冲, 戴福初, 徐锡伟.汶川地震滑坡灾害研究综述[J].地质论评, 2010, 56(6):860~874. https://www.cnki.com.cn/huiyi-DZDQ201101002034.htmlXU Chong, DAI Fuchu, XU Xiwei. Wenchuan earthquake-induced landslides:an overview[J]. Geological Review, 2010, 56(6):860~874. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/huiyi-DZDQ201101002034.html [5] 杨志华, 张永双, 郭长宝, 等.基于Newmark模型的尼泊尔MS 8.1级地震滑坡危险性快速评估[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(1):115~124. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170107&flag=1YANG Zhihua, ZHANG Yongshuang, GUO Changbao, et al. Landslide hazard rapid assessment in the MS 8.1 Nepal earthquake-impacted area, based on Newmark model[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(1):115~124. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170107&flag=1 [6] Newmark N M. Effects of earthquakes on dams and embankment[J]. Geotechnique, 1965, 18(2):139~160. http://geotip.igt.ethz.ch/.../Literatur/2012/Newmark_1965_erthquake_dams.pdf [7] Jibson R W, Harp E L, Michael J A. A method for producing digital probabilistic seismic landslide hazard maps[J]. Engineering Geology, 2000, 58(3~4):271~289. https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1998/ofr-98-113/ofr-98-113.pdf [8] 石菊松, 张永双, 董诚, 等.基于GIS技术的巴东新城区滑坡灾害危险性区划[J].地球学报, 2005, 26(3):275~282. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200503014SHI Jusong, ZHANG Yongshuang, DONG Cheng, et al. GIS-based landslide hazard zonation of the new Badong county site[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2005, 26(3):275~282. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200503014 [9] Jibson R W. Methods for assessing the stability of slopes during earthquakes-a retrospective[J]. Engineering Geology, 2011, 122(1/2):43~50. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013795210001936 [10] 王涛, 吴树仁, 石菊松, 等.地震滑坡危险性概念和基于力学模型的评估方法探讨[J].工程地质学报, 2015, 23(1):93~104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201501019.htmWANG Tao, WU Shuren, SHI Jusong, et al. Concepts and mechanical assessment method for seismic landslide hazard:a review[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(1):93~104. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201501019.htm [11] Godt J, șener B, Verdin K, et al. Rapid assessment of earthquake-induced landsliding[A]. Proceedings of the First World Landslide Forum[C]. Tokyo: United Nations University, 2008. [12] Del Gaudio V, Pierri P, Wasowski J. An approach to time-probabilistic evaluation of seismically induced landslide hazard[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2003, 93(2):557~569. doi: 10.1785/0120020016 [13] 刘甲美, 高孟潭, 吴树仁.概率性地震滑坡危险性区划方法及其应用[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(S1):3100~3110. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yslx2016s1058&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQLIU Jiamei, GAO Mengtan, WU Shuren. Probabilistic seismic landslide hazard zonation method and its application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(S1):3100~3110. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yslx2016s1058&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [14] 王涛, 吴树仁, 石菊松, 等.历史强震对渭河中游群发大型滑坡的诱发效应反演[J].地球学报, 2015, 36(3):353~361. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2015.03.10WANG Tao, WU Shuren, SHI Jusong, et al. Inversion of the inducing effects of historical strong earthquakes on large-scale landslides around the middle reaches of the Weihe River[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2015, 36(3):353~361. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2015.03.10 [15] 宋志, 倪化勇, 周洪福, 等.基于多层次物理力学参数的小区域地震滑坡危险性评估——以长江上游石棉县城及周边为例[J].地质力学学报, 2016, 22(3):760~770. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160329&flag=1SONG Zhi, NI Huayong, ZHOU Hongfu, et al. Risk assessment of seismic landslide within small region based on multi-level physical and mechanical parameters:a case study of Shimian and adjacent areas in the upper reaches of Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(3):760~770. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160329&flag=1 [16] Ambraseys N N, Menu J M. Earthquake-induced ground displacements[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 1988, 16(7):985~1006. doi: 10.1002/eqe.4290160704/abstract [17] Jibson R W. Predicting earthquake-induced landslide displacements using Newmark's sliding block analysis[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1993, (1411):9~17. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.733.2736 [18] Bray J D, Rathje E M. Earthquake-induced displacements of solid-waste landfills[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 1998, 124(3):242~253. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1998)124:3(242) [19] Jibson R W. Regression models for estimating coseismic landslide displacement[J]. Engineering Geology, 2007, 91(2/4):209~218. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.706.2379&rep=rep1&type=pdf [20] Hsieh S Y, Lee C T. Empirical estimation of the Newmark displacement from the Arias Intensity and critical acceleration[J]. Engineering Geology, 2011, 122(1/2):34~42. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013795210002577 [21] Chousianitis K, Del Gaudio V, Kalogeras I, et al. Predictive model of Arias Intensity and Newmark displacement for regional scale evaluation of earthquake-induced landslide hazard in Greece[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2014, 65:11~29. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2014.05.009 [22] Yuan R M, Deng Q H, Cunningham D, et al. Newmark displacement model for landslides induced by the 2013Ms7.0 Lushan earthquake, China[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2016, 10(4):740~750. doi: 10.1007/s11707-015-0547-y [23] Capolongo D, Refice A, Mankelow J. Evaluating earthquake-triggered landslide hazard at the basin scale through GIS in the upper Sele River valley[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2002, 23(6):595~625. doi: 10.1023/A:1021235029496 [24] Refice A, Capolongob A. Probabilistic Modeling of Uncertainties in Earthquake-induced landslide hazard assessment[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2002, 28(6):735~749. http://www.academia.edu/780016/Probabilistic_modeling_of_uncertainties_in_earthquake-induced_landslide_hazard_assessment_1 [25] Murphy W, Mankelow J M. Obtaining probabilistic estimates of displacement on a landslide during future earthquakes[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 2004, 8(1):133~157. doi: 10.1142/S1363246904001432 [26] Mahdavifar M, Jafari M K, Zolfaghari M R. Real-time generation of arias intensity and seismic landslides hazards maps using GIS[J]. Journal of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering, 2008:10(2):81~90. http://www.sid.ir/En/Journal/ViewPaper.aspx?FID=86020080203 [27] 王涛, 吴树仁, 石菊松, 等.基于简化Newmark位移模型的区域地震滑坡危险性快速评估——以汶川Ms8.0级地震为例[J].工程地质学报, 2013, 21(1):16~24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201301004.htmWANG Tao, WU Shuren, Shi Jusong, et al. Case study on rapid assessment of regional seismic landslide hazard based on simplified Newmark displacement model:Wenchuan Ms8.0 earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(1):16~24. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201301004.htm [28] 陈晓利, 袁仁茂, 庾露. Newmark方法在芦山地震诱发滑坡分布预测研究中的应用[J].地震地质, 2013, 35(3):661~670. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201303019.htmCHEN Xiaoli, YUAN Renmao, YU Lu. Applying the Newmark's model to the assessment of earthquake-triggered landslides during the lushan earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2013, 35(3):661~670. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201303019.htm [29] 葛华, 陈启国, 王德伟.地震滑坡危险性评价及编图——以映秀震中区为例[J].中国地质, 2013, 40(2):644~652. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201302029.htmGE Hua, CHEN Qiguo, WANG Dewei. The assessment and mapping of seismic landslide hazards:a case study of Yingxiu area, Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 2013, 40(2):644~652. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201302029.htm [30] Liu J M, Gao M T, Wu S R, et al. A hazard assessment method for potential earthquake-induced landslides-a case study in Huaxian County, Shaanxi province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2016, 90(2):590~603. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2016.90.issue-2 [31] 雷中生, 袁道阳, 葛伟鹏, 等. 734年天水7级地震考证与发震构造分析[J].地震地质, 2007, 29(1):51~62. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/95728X/200701/24197791.htmlLEI Zhongsheng, YUAN Daoyang, GE Weipeng, et al. Textual research on the Tianshui M 7 earthquake in 734 ad and analysis of its causative structure[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2007, 29(1):51~62. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/qk/95728X/200701/24197791.html [32] 杨晓平, 冯希杰, 黄雄南, 等.礼县-罗家堡断裂晚第四纪活动特征:兼论1654年礼县8级地震孕震机制[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(2):504~519. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150214YANG Xiaoping, FENG Xijie, HUANG Xiongnan, et al. The late quaternary activity characteristics of the Lixian-Luojiabu fault:a discussion on the seismogenic mechanism of the Lixian M 8 earthquake in 1654[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(2):504~519. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg20150214 [33] 袁道阳, 雷中生, 王爱国. 1654年甘肃天水南8级地震补充考证[J].地震工程学报, 2017, 39(3):509~520. https://mall.cnki.net/lunwen-1017056430.htmlYUAN Daoyang, LEI Zhongsheng, WANG Aiguo. Additional textual criticism of southern Tianshui M8 earthquake in Gansu Province in 1654[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2017, 39(3):509~520. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://mall.cnki.net/lunwen-1017056430.html [34] Liu J M, Shi J S, Wang T, et al. Seismic landslide hazard assessment in the Tianshui area, China, based on scenario earthquakes[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2017, doi:10.1007/s10064~016~0998~8. (inPress) [35] 刘甲美, 王涛, 石菊松, 等.四川九寨沟Ms7.0级地震滑坡应急快速评估[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(5):639~645. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170501&flag=1LIU Jiamei, WANG Tao, SHI Jusong, et al. Emergency rapid assessment of landslides induced by the Jiuzhaigou Ms7.0 earthquake, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(5):639~645. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170501&flag=1 [36] 段汝文, 王峻, 李兰.黄土的物理力学指标与黄土易损性分析研究[J].西北地震学报, 1997, 19(3):81~85. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=2696572DUAN Ruwen, WANG Jun, LI Lan. On relationship between physical mechanical indices and vulnerability of loess[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 1997, 19(3):81~85. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=2696572 [37] Zhang Z L, Wang T, Wu S R, et al. Dynamics stress-strain behavior of Tianshui soils[J]. Landslides, 2017, 14(1):323~335, doi: 10.1007/s10346~016~0694~6. [38] Zhang Z L, Wang T, Wu S R, et al. Seismic performance of loess-mudstone slope by centrifuge tests[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2017, 76(2):671~679, doi: 10.1007/s10064~015~0846~2. [39] 董瑞树, 冉洪流, 高铮.中国大陆地震震级和地震活动断层长度的关系讨论[J].地震地质, 1993, 15(4):395~400. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ199304020.htmDONG Ruishu, RAN Hongliu, GAO Zheng. The relationship between earthquake magnitude and length of active fault in China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1993, 15(4):395~400. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ199304020.htm [40] 孟令媛, 周龙泉, 刘杰. 2013年四川芦山MS7.0地震近断层强地面运动模拟及烈度分布估计[J].地球物理学报, 2014, 57(2):441~448. doi: 10.6038/cjg20140210MENG Lingyuan, ZHOU Longquan, LIU Jie. Estimation of the near-fault strong ground motion and intensity distribution of the 2013 Lushan, Sichuan, MS7.0 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(2):441~448. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg20140210 [41] Travasarou T, Bray J D, Abrahamson N A. Empirical attenuation relationship for arias intensity[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2003, 32(7):1133~1155. http://peer.berkeley.edu/research/peertestbeds/Cct/Bray%2024%20May%202002%20Arias%20Intensity%20Attenuation.pdf [42] Legg M, Slosson J, Eguchi R. Seismic hazard for lifelines vulnerability analyses[A]. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Microzonation[C]. Seattle, Washington, 1982. -





 下载:
下载: