THE EFFICIENT MECHANISMS FOR PRECIPITATING WOLFRAMITE: CO2 ESCAPING
-
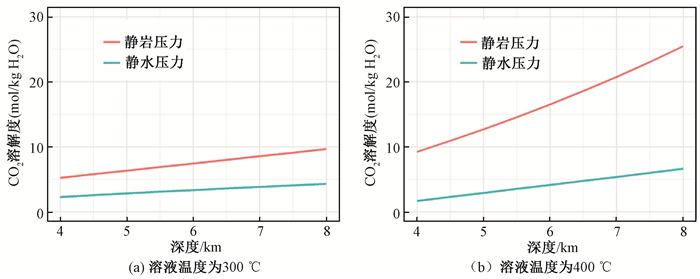
摘要: 黑钨矿是石英脉钨矿床的主要矿石矿物,其沉淀机制一直存在争议。CO2逃逸能否造成黑钨矿有效沉淀尚缺乏定量模型的评价。文章建立了W-Fe-Cl-Na-O-C-H体系的反应平衡模型,涉及22种组分和16个化学反应;相关热力学参数来自SUPCRT数据库。模型计算结果表明,pH与流体压力呈负相关关系,而钨溶解度与流体压力呈正相关关系;当成矿流体压力从静岩压力降至静水压力水平,钨溶解度降幅可达到27%~47%,降幅与温度和深度成正比。因而,降压造成的CO2逃逸是黑钨矿沉淀的有效机制之一。Abstract: Wolframite is the main ore mineral of vein-type tungsten deposits. How wolframite precipitates from hydrothermal fluids is highly disputed in the literature. Whether CO2 escaping causes significant precipitationof wolframitehas not been quantitatively examined. A reaction equilibrium model for the system of W-Fe-Na-Cl-H-C-O was established in this contribution. The model contains 22 species and 16 reactions, the thermodynamic data of which are from the database SUPCRT. The modeling results indicate that pH is negatively correlated to fluid pressure and tungsten solubility is positively correlated to fluid pressure. A decreasein fluid pressure from lithostatic to hydrostatic level could cause a drop of tungsten solubility by 27%~47%, and the decrease degree has a positive correlation to temperature and depth. Therefore, CO2 escaping accompanying a drop of fluid pressure is one of the mechanisms precipitating wolframite efficiently.
-
Key words:
- wolframite /
- precipitation mechanism /
- CO2 escaping /
- equilibrium reaction modeling
-
表 1 平衡反应模型中的16个化学反应
Table 1. The 16 reactions used in the thermodynamic model of this study
序号 化学反应 1 H++WO42-=HWO4- 2 H++HWO4-=H2WO40 3 H++Cl=HCl0 4 H2O=H++OH- 5 FeWO4(s)=Fe2++WO42- 6 Fe2++Cl=FeCl+ 7 Fe2++2Cl=FeCl20 8 Fe2++H2O=FeOH++H+ 9 Fe2++H2O=FeO0+2H+ 10 Fe2++2H2O=HFeO2-+3H+ 11 Na++Cl-=NaCl0 12 Na++H2O=NaOH0+H+ 13 Na++WO42-=NaWO4- 14 Na++HWO4-=NaHWO40 15 CO2 (aq)+H2O=HCO3-+H+ 16 HCO3-=CO32-+H+ 表 2 平衡反应模型中所用的电荷和质量平衡方程
Table 2. Mass and charge balance constraints used in the thermodynamic model
序号 名称 电荷和质量平衡方程 17 电荷平衡方程 [H+]+[Na+]+[FeCl+]+2[Fe2+]+[FeOH+]=[HWO4-]+2[WO42-]+[Cl-]+[OH-]+[HFeO2-]+[HCO3-]+2[CO32-] 18 氯质量平衡方程 ΣCl=[Cl-]+[HCl0]+[NaCl0]+[FeCl+]+2[FeCl20] 19 ΣFe=ΣW [H2WO40]+[HWO4-]+[WO42-]=[FeCl+]+[FeCl20]+[Fe2+]+[FeOH+]+[FeO0]+[HFeO2-] 20 CO2含量固定 在给定的温度、压力和盐度条件下,CO2含量达到溶解度(根据文献[53]公式计算) -
[1] Mao J W, Cheng Y B, Chen M H, et al. Major types and time-space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2013, 48(3):267~294. doi: 10.1007/s00126-012-0446-z [2] 陈毓川, 裴荣富, 张宏良, 等.南岭地区与中生代花岗岩类有关的有色及稀有金属矿床地质[M].北京:地质出版社, 1989.CHEN Yuchuan, PEI Rongfu, ZHANG Hongliang, et al. The geology of nonferrous and rare metal deposits related to Mesozoic Granitoids in Nanling Region, China[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing Housing, 1989. (in Chinese) [3] 柳志青.脉状钨矿床成矿预测理论[M].北京:科学出版社, 1980.LIU Zhiqing. Metallogenic prognosis of vein-type tungsten deposits[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1980. (in Chinese) [4] 朱焱龄, 李崇佑, 林运淮.赣南钨矿地质[M].南昌:江西人民出版社, 1981.ZHU Yanling, LI Chongyou, LIN Yunhuai. Tungsten deposit geology in South Jiangxi Province[M]. Nanchang:Jiangxi People's Publishing House, 1981. (in Chinese) [5] 刘向冲.江西大吉山石英脉型黑钨矿床"五层楼"垂直形态分带动力学机制[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-11415-1015518056.htmLIU Xiangchong. The mechanisms of the five-floor vertical morphological zonation at the Dajishan vein-type tungsten deposit, Jiangxi[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014. (in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-11415-1015518056.htm [6] 祝新友, 王京彬, 王艳丽, 等.论石英脉型钨矿成矿系统的相对封闭性——以湖南瑶岗仙脉型钨矿床为例[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(5):825~835. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201405002ZHU Xinyou, WANG Jingbin, WANG Yanli, et al. Relative closed ore-forming system in the tungsten-bearing quartz vein:a case study of the Yaogangxian deposit, Hunan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(5):825~835. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201405002 [7] 张德会.岩浆-热液过渡性流体及其成矿效应[A].中国矿物岩石地球化学学会学术年会[C].宁波, 2003. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD200309002080.htmZHANG Dehui. Magmatic-hydrothermal transitional fluids and its mineralization effect[A]. The Annual conference of Chinese Society for Minerology, Petrology, and Geochemistry[C]. Ningbo, 2003. (in Chinese) http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD200309002080.htm [8] Ni P, Wang X D, Wang G G, et al. An infrared microthermometric study of fluid inclusions in coexisting quartz and wolframite from Late Mesozoic tungsten deposits in the Gannan metallogenic belt, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65:1062~1077. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.08.007 [9] 曹晓峰, 吕新彪, 何谋春, 等.共生黑钨矿与石英中流体包裹体红外显微对比研究——以瑶岗仙石英脉型钨矿床为例[J].矿床地质, 2009, 28(5):611~620. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.05.007CAO Xiaofeng, LV Xinbiao, HE Mouchun, et al. An infrared microscope investigation of fluid inclusions in coexisting quartz and wolframite:A case study of Yaogangxian quartz-vein wolframite deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2009, 28(5):611~620. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.05.007 [10] Wei W F, Hu R Z, Bi X W, et al. Infrared microthermometric and stable isotopic study of fluid inclusions in wolframite at the Xihuashan tungsten deposit, Jiangxi province, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47(6):589~605. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0377-0 [11] Lecumberri-Sanchez P, Vieira R, Heinrich C A, et al. Fluid-rock interaction is decisive for the formation of tungsten deposits[J]. Geology, 2017, 45(7):579~582. doi: 10.1130/G38974.1 [12] Polya D A. Pressure-Independence of Wolframite solubility for Hydrothermal Vein Formation[J]. Transactions of the Institution of Mining and Metellurgy, 1990, 99(B59):120~124. [13] Korges M, Weis P, Lüders V, et al. Depressurization and boiling of a single magmatic fluid as a mechanism for tin-tungsten deposit formation[J]. Geology, 2017, 46(1):75~78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f71720d608f9ad3bf477f9d9edc317c4 [14] 张生, 陈根文.钨的气态迁移与岩浆-热液成矿作用:实验研究及其成矿学意义[J].地质科学, 2015, 50(3):898~910. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2015.03.015ZHANG Sheng, CHEN Genwen. Gaseous transport and magmatic-hydrothermal mineralization of tungsten:experimental study and its metallogenic implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2015, 50(3):898~910. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2015.03.015 [15] Xiong Y Q, Shao Y J, Zhou H D, et al. Ore-forming mechanism of quartz-vein-type W-Sn deposits of the Xitian district in SE China:Implications from the trace element analysis of wolframite and investigation of fluid inclusions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 83:152~173. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.12.007 [16] 王旭东, 倪培, 张伯声, 等.江西盘古山石英脉型钨矿床流体包裹体研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(5):539~550. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.05.009WANG Xudong, NI Pei, ZHANG Bosheng, et al. Fluid inclusion studies of the Pangushan quartz-vein type tungsten deposit in southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Et Mineralogica, 2010, 29(5):539~550. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.05.009 [17] 席斌斌, 张德会, 周利敏, 等.江西省全南县大吉山钨矿成矿流体演化特征[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(7):956~966. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.07.014XI Binbin, ZHANG Dehui, ZHOU Limin, et al. Characteristics of ore-forming fluid evolution in Dajishan tungsten deposit, Quannan County, Jiangxi[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(7):956~966. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.07.014 [18] 周龙全, 李光来, 苏晔, 等.赣南茅坪钨矿床黄玉单晶流体包裹体研究[J].矿床地质, 2017, 36(4):921~934. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz201704009ZHOU Longquan, LI Guanglai, SU Ye, et al. A preliminary study of fluid inclusions of topaz crystal from Maoping tungsten deposit, southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2017, 36(4):921~934. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz201704009 [19] Liu X C, Xing H L, Zhang D H. Influences of hydraulic fracturing on fluid flow and mineralization at the vein-type tungsten deposits in southern China[J]. Geofluids, 2017, 2017:Article ID 4673421. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d68663d75625e0b58e8d3f74c597d535&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [20] 祝新友, 王京彬, 王艳丽, 等.南岭锡钨多金属矿区碱长花岗岩的厘定及其意义[J].中国地质, 2012, 39(2):359~381. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.02.009ZHU Xinyou, WANG Jingbin, WANG Yanli, et al. Characteristics of alkali feldspar granite in tungsten (tin) deposits of Nanling region[J]. Geology in China, 2012, 39(2):359~381. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.02.009 [21] 古菊云.华南钨矿脉的形态分类[A].钨矿地质讨论会论文集[C].北京: 地质出版社, 1984, 35~45.Gu Juyun. Morphological zonation of tungsten deposits in South China[A]. Proceedings of Symposium on Tungsten Geology[C]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1984, 35~45. (in Chinese) [22] 刘向冲, 张德会, 赵波, 等.漂塘钨矿床"五层楼"垂直形态分带定量分析[J].高校地质学报, 2017, 23(3):408~416. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb201703004LIU Xiangchong, ZHANG Dehui, ZHAO Bo, et al. Quantitative analysis of the "five-floor" vertical morphological zonation in the Piaotang tungsten deposits, South China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2017, 23(3):408~416. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb201703004 [23] 李吉明, 李永明, 楼法生, 等.赣北发现"五层楼"式石英脉型黑钨矿矿床——东坪黑钨矿矿床的发现及其地质意义[J].地球学报, 2016, 37(3):379~384. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201603015LI Jiming, LI Yongming, LOU Fasheng, et al. A "five-storey" style quartz vein wolframite deposit in northern Jiangxi province:the discovery of the dongping wolframite deposit and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2016, 37(3):379~384. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201603015 [24] 董少花, 毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 等.湖南瑶岗仙石英脉型黑钨矿床成矿流体特征[J].矿物岩石, 2011, 31(2):54~60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2011.02.008DONG Shaohua, BI Xianwu, HU Ruizhong, et al. Characteristics of ore-forming fluid in Yaogangxian quartz-vein wolframite deposit, Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2011, 31(2):54~60. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2011.02.008 [25] 王巧云, 胡瑞忠, 彭建堂, 等.湖南瑶岗仙钨矿床流体包裹体特征及其意义[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(9):2263~2273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.09.024WANG Qiaoyun, HU Ruizhong, PENG Jiantang, et al. Characteristics and significance of the fluid inclusions from Yaogangxian tungsten deposit in south of Hunan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(9):2263~2273. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.09.024 [26] 叶诗文, 路远发, 童启荃, 等.盘古山钨矿成矿流体特征及其地质意义[J].华南地质与矿产, 2014, 30(1):26~35. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hndzykc201401004YE Shiwen, LU Yuanfa, TONG Qiquan, et al. Fluid inclusion characteristic and its geological implication of the Pangushan tungsten deposit[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2014, 30(1):26~35. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hndzykc201401004 [27] 宋生琼, 胡瑞忠, 毕献武, 等.赣南淘锡坑钨矿床流体包裹体地球化学研究[J].地球化学, 2011, 40(3):237~248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201103003SONG Shengqiong, HU Ruizhong, BI Xianwu, et al. Fluid inclusion geochemistry of the Taoxikeng tungsten deposit in southern Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Geochimica, 2011, 40(3):237~248. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201103003 [28] 宋生琼, 胡瑞忠, 毕献武, 等.赣南崇义淘锡坑钨矿床氢、氧、硫同位素地球化学研究[J].矿床地质, 2011, 30(1):1~10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.01.001SONG Shengqiong, HU Ruizhong, BI Xianwu, et al. Hydrogen, oxygen and sulfur isotope geochemical characteristics of Taoxikeng tungsten deposit in Chongyi County, Southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(1):1~10. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.01.001 [29] 王旭东, 倪培, 蒋少涌, 等.赣南漂塘钨矿流体包裹体研究[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(9):2163~2170. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200809025WANG Xudong, NI Pei, JIANG Shaoyong, et al. Fluid inclusion study on the Piaotang tungsten deposit, southern Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(9):2163~2170. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200809025 [30] 王旭东, 倪培, 袁顺达, 等.赣南漂塘钨矿锡石及共生石英中流体包裹体研究[J].地质学报, 2013, 87(6):850~859. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.06.009WANG Xudong, NI Pei, YUAN Shunda, et al. Fluid inclusion studies on coexisting cassiterite and quartz from the Piaotang tungsten deposit, Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(6):850~859. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.06.009 [31] 王旭东, 倪培, 袁顺达, 等.江西黄沙石英脉型钨矿床流体包裹体研究[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(1):122~132. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201201010WANG Xudong, NI Pei, YUAN Shunda, et al. Fluid inclusion studies of the Huangsha quartz-vein type tungsten deposit, Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(1):122~132. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201201010 [32] 黄惠兰, 常海亮, 付建明, 等.西华山脉钨矿床的形成压力及有关花岗岩的侵位深度[J].矿床地质, 2006, 25(5):562~571. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.05.003HUANG Huilan, CHANG Hailiang, FU Jianming, et al. Formation pressure of wolframite-vein deposits and emplacement depth of related granite in Xihuashan, Jiangxi Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25(5):562~571. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.05.003 [33] 王碟, 卢焕章, 毕献武.与花岗质岩浆系统有关的石英脉型钨矿和斑岩型铜矿成矿流体特征比较[J].地学前缘, 2011, 18(5):121~131. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201105012WANG Die, LU Huanzhang, BI Xianwu. Comparison of characteristics of ore forming fluids between quartz-vein tungsten deposits and porphyry copper deposits associated with granitic rocks[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(5):121~131. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201105012 [34] 芮宗瑶, 李荫清, 王龙生, 等.从流体包裹体研究探讨金属矿床成矿条件[J].矿床地质, 2003, 22(1):13~23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2003.01.002RUI Zongyao, LI Yinqing, WANG Longsheng, et al. Approach to ore-forming conditions in light of ore fluid inclusions[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2003, 22(1):13~23. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2003.01.002 [35] Chen L L, Ni P, Li W S, et al. The link between fluid evolution and vertical zonation at the Maoping tungsten deposit, Southern Jiangxi, China:Fluid inclusion and stable isotope evidence[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 192:18~32. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.01.001 [36] Li W S, Ni P, Pan J Y, et al. Fluid inclusion characteristics as an indicator for tungsten mineralization in the Mesozoic Yaogangxian tungsten deposit, central Nanling district, South China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 192:1~17. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.11.013 [37] 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨进辉, 等.胶东中生代构造体制转折过程中流体演化和金的大规模成矿[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21(5):1317~1328. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200505001FAN Hongrui, HU Fangfang, YANG Jinhui, et al. Fluid evolution and large-scale gold metallogeny during Mesozoic tectonic transition in the eastern Shandong province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(5):1317~1328. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200505001 [38] 倪培, 迟哲, 潘君屹, 等.热液矿床的成矿流体与成矿机制——以中国若干典型矿床为例[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2018, 37(3):369~395. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb201803002NI Pei, CHI Zhe, PAN Junyi, et al. The characteristics of ore-forming fluids and mineralization mechanism in hydrothermal deposits:a case study of some typical deposits in China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2018, 37(3):369~395. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb201803002 [39] 徐九华, 张国瑞, 魏浩, 等.脉状金矿床的成矿压力与深度:流体包裹体方法及其影响因素[J].南京大学学报(自然科学), 2012, 48(3):266~277. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/njdxxb201203004XU Jiuhua, ZHANG Guorui, WEI Hao, et al. Ore-forming pressures and depths of vein gold deposits:fluid inclusion studies and their influence factors[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 2012, 48(3):266~277. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/njdxxb201203004 [40] 冷成彪, 张兴春, 王守旭, 等.岩浆-热液体系成矿流体演化及其金属元素气相迁移研究进展[J].地质论评, 2009, 55(1):100~112. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2009.01.012LENG Chengbiao, ZHANG Xingchun, WANG Shouxu, et al. Advances of researches on the evolution of ore-forming fluids and the vapor transport of metals in magmatic-hydrothermal systems[J]. Geological Review, 2009, 55(1):100~112. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2009.01.012 [41] 陈家玮, 鲍征宇.地球化学反应平衡模型的建模方法[J].地质科技情报, 2001, 20(3):41~46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2001.03.009CHEN Jiawei, BAO Zhengyu. Approaches to geochemical reaction equilibrium modeling[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2001, 20(3):41~46. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2001.03.009 [42] 周涛发, 刘晓东, 袁峰, 等.安徽月山矿田成矿流体中铜、金的迁移形式和沉淀的物理化学条件[J].岩石学报, 2000, 16(4):551~558. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200004014ZHOU Taofa, LIU Xiaodong, YUAN Feng, et al. Migrating forms and depositional physicochemical conditions of copper, gold in hydrothermal solutions of Yueshan orefield, Anhui province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2000, 16(4):551~558. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200004014 [43] 周涛发, 袁峰, 岳书仓, 等.安徽月山矿田夕卡岩型矿床形成的水岩作用[J].矿床地质, 2002, 21(1):1~9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2002.01.001ZHOU Taofa, YUAN Feng, YUE Shucang, et al. Water/rock interaction during formation of skarn-type deposits in Yueshan Orefield, Anhui Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2002, 21(1):1~9. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2002.01.001 [44] Heinrich C A. The physical and chemical evolution of low-salinity magmatic fluids at the porphyry to epithermal transition:a thermodynamic study[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2005, 39(8):864~889. doi: 10.1007/s00126-004-0461-9 [45] Aghbelagh Y B, Yang J W. Effect of graphite zone in the formation of unconformity-related uranium deposits:Insights from reactive mass transport modeling[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 144:12~27. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.01.020 [46] Aghbelagh Y B, Yang J W. Role of hydrodynamic factors in controlling the formation and location of unconformity-related uranium deposits:insights from reactive-flow modeling[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2017, 25(2):465~486. doi: 10.1007/s10040-016-1485-9 [47] Hofstra A H, Leventhal J S, Northrop H R, et al. Genesis of sediment-hosted disseminated-gold deposits by fluid mixing and sulfidization:Chemical-reaction-path modeling of ore-depositional processes documented in the Jerritt Canyon district, Nevada[J]. Geology, 1991, 19(1):36~40. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b9c87699886c986abdd96ff46d887b9d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [48] Heinrich C A. The chemistry of hydrothermal tin(-tungsten) ore deposition[J]. Economic Geology, 1990, 85(3):457~481. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.85.3.457 [49] Gibert F, Moine B, Schott J, et al. Modeling of the transport and deposition of tungsten in the scheelite-bearing calc-silicate gneisses of the Montagne Noire, France[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1992, 112(2~3):371~384. doi: 10.1007/BF00310467 [50] 龚庆杰, 於崇文, 张荣华.柿竹园钨多金属矿床形成机制的物理化学分析[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(4):617~625. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.029GONG Qingjie, YU Chongwen, ZHANG Ronghua. Physical chemistry study on the ore-forming process of Shizhuyuan tungsten-polymetallic deposit[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(4):617~625. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.029 [51] Wood S A, Samson I M. The hydrothermal geochemistry of Tungsten in Granitoid environments:I. Relative solubilities of ferberite and scheelite as a function of T, P, pH, and mNaCl[J]. Economic Geology, 2000, 95(1):143~182. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.95.1.143 [52] Johnson J W, Oelkers E H, Helgeson H C. SUPCRT92:A software package for calculating the standard molal thermodynamic properties of minerals, gases, aqueous species, and reactions from 1 to 5000 bar and 0 to 1000℃[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 1992, 18(7):899~947. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0229307581/ [53] Mao S D, Zhang D H, Li Y Q, et al. An improved model for calculating CO2 solubility in aqueous NaCl solutions and the application to CO2-H2O-NaCl fluid inclusions[J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 347:43~58. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.03.010 [54] Helgeson H C. Thermodynamics of hydrothermal systems at elevated temperatures and pressures[J]. American Journal of Science, 1969, 267(7):729~804. doi: 10.2475/ajs.267.7.729 [55] Drummond S E Jr. Boiling and mixing of hydrothermal fluids: chemical effects on mineral precipitation[D]. Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania State University, 1981. [56] Polya D A. Efficiency of hydrothermal ore formation and the Panasqueira W-Cu(Ag)-Sn vein deposit[J]. Nature, 1988, 333(6176):838~841. doi: 10.1038/333838a0 -





 下载:
下载: