QUANTITATIVE CALCULATIONS OF ENVIRONMENTAL DOSE RATE AT DIFFERENT INFLUENCING FACTORS IN LUMINESCENCE DATING
-
摘要: 释光测年中影响环境剂量率(D)的主要因素包括含水量、宇宙射线、a值(α辐射相对于γ辐射产生释光的效率)和氡逃逸等。为研究这些影响因素对D值的影响程度,采用不同的参数值对一个假定U、Th和K含量已知的样品进行了较详细的定量计算。研究结果表明,含水量变化对环境剂量率影响最大,影响程度甚至可达50%以上;其次为宇宙射线的影响,最大可达近15%;氡逃逸的影响最多不超过8%;而a值通常取固定值,产生的影响则相对小的多。Abstract: The environmental dose rate (D) in luminescence dating can be influenced by water content, cosmic ray, factor a, radon escape, etc. A series of detailed quantitative calculations were applied to the sample A1 with given U, Th and K content for D values using different parameter values of water content, cosmic rays, factor a. The calculations show that the greatest influence is up to 50% with the changes of water content, and the influence from cosmic rays is up to 15%. The influence from factor a is relatively smaller because it usually is a given constant value. The radon escape will bring an error no more than 8%.
-
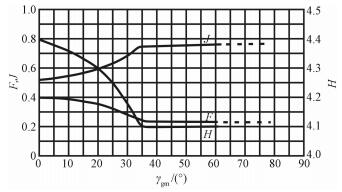
图 1 宇宙射线剂量率校正时地磁纬度与校正系数(F、J和H)的关系[5]
Figure 1. Relationship between geomagnetic latitudes and correction coefficients (F, J, H)
表 2 样品A1环境剂量率计算参数
Table 2. Parameters for the calculation of environmental dose rate of sample A1

表 3 样品A1环境剂量率计算结果
Table 3. Results of environmental dose rate for sample A1

表 4 不同经度、纬度时的地磁纬度值
Table 4. The geomagnetic latitude at different longitude and latitude

表 5 北纬15°线不同海拔不同埋深时的Dc值
Table 5. The Dc under different altitudes and depths at 15°N

表 6 北纬35°线不同海拔不同埋深时的Dc值
Table 6. The Dc under different altitudes and depths at 35°N

表 7 北纬55°线不同海拔不同埋深时的Dc值
Table 7. The Dc under different altitudes and depths at 55°N

表 8 不同Fw值、不同含水量时样品A1的D值
Table 8. The D under different water content and different Fw for sample A1

-
[1] Huntley D J, Godfrey-Smith D I, Thewalt M L W. Optical dating of sediments[J].Nature, 1985, 313:105~107. doi: 10.1038/313105a0 [2] Aitken M J.Thermoluminescence dating[M].London:Academic Press, 1985:83~95, 280~305. [3] Aitken M J.An introduction to optical dating[M].London:Oxford University Press, 1998:39~44. [4] 王维达, 金嗣炤, 高钧成.中国热释光与电子自旋共振:测定年代研究[M].北京:中国计量出版社, 1997.WANG Wei-da, JIN Si-shao, GAO Jun-cheng.Study of thermoluminescence and electron spin resonance dating of China[M].Beijing:China Metrology Publishing House, 1997. [5] Prescott J R, Hutton J T.Cosmic ray contributions to dose rates for luminescence and ESR dating:Large depths and long-term time variations[J].Radiation Measurements, 1994, 23:497~500. doi: 10.1016/1350-4487(94)90086-8 [6] Zimmerman D W.Thermoluminescence dating using fine grains from pottery[J].Archaeometry, 1971, 13:29~52. doi: 10.1111/arch.1971.13.issue-1 [7] 王同利, 陈杰, 杨传成.Daybreak厚源α-计数仪的标定及测量影响因素的初步研究[J].地震地质, 2005, 27(4):623~644. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200504013.htmWANG Tong-li, CHEN Jie, YANG Chuan-cheng.Calibration of daybreak thick source alpha counter and preliminary study of influencing factors[J].Seismology and Geology, 2005, 27(4):623~644. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200504013.htm -





 下载:
下载: